Oxides of Nitrogen
Table of Content |
Nitrogen forms various oxides that display an extensive variety of oxidation states.
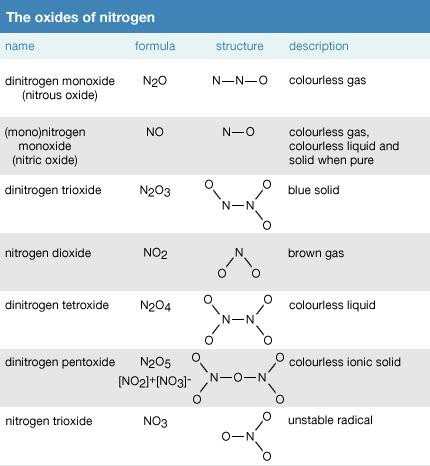
Oxides of Nitrogen
Fig. 1: Different oxides of nitrogen showing their formula, structure and description
Fig. 2: Oxides of Nitrogen Showing Bond Angles and Bond Length
Nitrous Oxide or Dinitrogen Oxide (N2O)
Nitrous Oxide is also known as Laughing Gas. It is generally arranged by warming ammonium nitrate slowly to 240°C. It is a dismal gas that is genuinely dissolvable in icy water and the minimally dissolvable in boiling hot water.
Nitrous oxide is a neutral oxide. Nitrous oxide is a molecule with linear shape and is a resonance hybrid of two structures.
The bond lengths in the atom are 113 per molecule and 119 per molecule.
Fig. 3: Resonance forms of Nitrous Oxide
Nitrogen Monoxide or Nitric Oxide (NO)
Nitrogen Monoxide can be manufactured by the reduction of nitrite salt with ferrous sulphate.

Nitric Oxide is a colorless gas that achieves blue shading when melted. It is sparingly solvent in water. It is likewise a neutral oxide. It is a molecule with linear shape and is a resonance hybrid of the two structures. The bond length is 115 pm which is intermediate between double bond and triple bond. Also it is paramagnetic in nature.
Fig. 4: Molecular formula, Structural formula and Molecular Model of Nitric Oxide
Dinitrogen Trioxide or Nitrogen Sesquioxide (N2O3)
It is acquired as a blue fluid when a combination of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide or dinitrogen tetra oxide is cooled to less than minus 20°C.

Dinitrogen trioxide is an anhydride of nitrous acid which is acidic in nature. It has a planar shape and is a resonance hybrid of the two forms as shown below.
Fig. 5: Resonance forms of Dinitrogen Trioxide
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
Nitrogen Dioxide can be prepared by heating lead nitrate at a temperature of about 673 K.

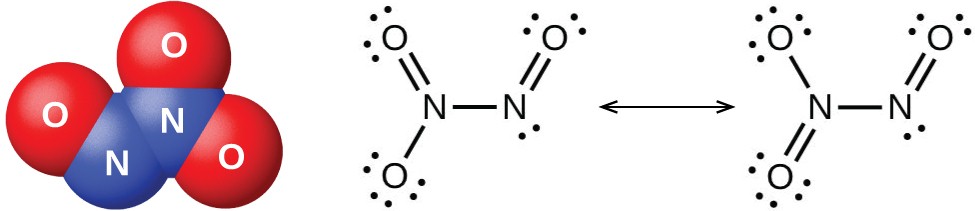
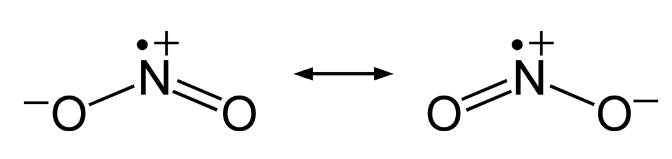
Nitrogen Dioxide is a gas that is brown in color is a combined anhydride of nitrous acid and nitric acid. It is an acidic oxide with angular shape. The bond angle is 134 degrees and bond length is 120 pm. The atom is found as a resonance hybrid and is a paramagnetic substance. Because of the nearness of unpaired electron it dimerise to a colorless dinitrogen tetroxide atom that has even number of electrons. At low temperatures, nitrogen dioxide partners to solid dinitrogen tetroxide.
Fig. 6: Bond Length and Bond Angle of Nitrogen Dioxide
Fig. 7: Resonance Hybrids of Nitrogen Oxides
Dinitrogen Pentoxide (N2O5)
Upon dehydration of nitric acid with phosphorus pentoxide, dinitrogen pentoxide is obtained.

It is a colourless crystalline deliquescent solid which readily dissolves in water to give nitric acid.
It is an anhydride of nitric acid which is acidic in nature. It has a planar shape and is a resonance hybrid of the two forms as shown below. The planar structure can be seen just in its vapor state, it is ionic in the solid state. The ionic solid is alluded to as nitronium nitrate.
Fig. 8: Bond Angles of Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Frquently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How are oxides of nitrogen formed?
Sol. In regions of high engine vehicle movement, for example, in vast urban areas, the measure of nitrogen oxides discharged into the climate as air contamination can be noteworthy. NOx gasses are framed at whatever point ignition happens within the sight of nitrogen – e.g. in auto motors; they are additionally produced by lightning.
Q2. Oxides of nitrogen effects?
Sol. Nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide together allude as oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx gasses react to frame exhaust cloud and acid rain and additionally being integral to the development of fine particles (PM) and ground level ozone, both of which are connected with adverse wellbeing impacts.
Q3. What is the chemical formula for nitrogen oxide?
Sol. It is Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Q4. What is a NOx emission?
Sol. NOx is a generic term for the mono-nitrogen oxides NO and NO2 (nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide). They are delivered from the reaction among nitrogen, oxygen and even hydrocarbons (amid burning), particularly at high temperatures. In zones of high engine vehicle movement, for example, in extensive urban communities, the measure of nitrogen oxides radiated into the air as air contamination can be huge. NOx gasses are shaped at whatever point burning happens within the sight of nitrogen – as in an air-breathing motor; they additionally are delivered by lightning.
Q5. Is nitrogen oxide harmful?
Sol. Nitrogen dioxide is an aggravation gas, which at high fixations causes irritation of the aviation routes.
At the point when nitrogen is discharged amid fuel burning it joins with oxygen iotas to make nitric oxide (NO). This further consolidates with oxygen to make nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Nitric oxide is not thought to be unsafe to wellbeing at run of the mill surrounding focuses, yet nitrogen dioxide can be. Nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide are alluded to together as oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
NOx gasses react to frame brown haze and acid rain and in addition being key to the development of fine particles (PM) and ground level ozone, both of which are connected with unfriendlyadverse wellbeing impacts.
Q6. Is NOx a green house gas?
Sol. Nitrogen oxides are a group of gases that are made out of nitrogen and oxygen. Two of the most widely recognized nitrogen oxides are nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide. The chemical equation for nitric oxide is NO; for nitrogen dioxide, it is NO2. Nitrous oxide, N2O, is a greenhouse gas that adds to environmental change.
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings