Oxoacids of Halogens
Table of Content |
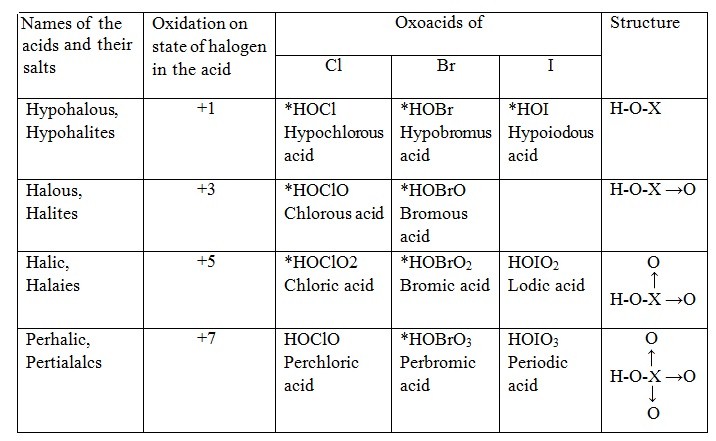
Halogens for the most part shape four arrangement of oxoacids, to be specific, hypohalous acids, halous acids, halic acids and perhalic acids where, X speaks any of the halogen, which might be fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine.
Oxidation States of the Four Series of Oxoacids
Fig. 1: Oxidation states of the 4 series of oxoacids
Structures of the Oxoacids of Halogens
In these oxoacids, the focal halogen molecule is sp3 hybridized.
One X-OH bond is basically present in each oxoacid. In the majority of these oxoacids, "X = O" bonds are available. The double bond introduced in an oxoacid between the focal halogen particle and oxygen is d pi - p pi in nature.
Hypohalous acids incorporate hypofluorous acid, hypochlorous acid, hypobromous acid and hypoiodous acid. The halogen has the oxidation condition of +1 in hypohalous acids.
The particular hypohalite particles have a linear shape attributable to the nearness of three lone pair of electrons on the focal halogen atom.
Fig. 2: Structures of oxoacids of chlorine
Fig. 3: Linear shape of hypohalite ions
Hypohalous acids, have a tendency of making halic acids as they are less stable.
3HOX → HOXO2 + 3HX
Hypohalous acid Halic acid Hydrogen halide
Fluorine has only one oxoacids that is hypofluorous acid. Due to the absence of d- orbitals in fluorine no higher oxoacid of fluorine is known.
Halous acids, incorporates just chlorous acid. The chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in chlorous acid. The chlorite particle has a V - shape inferable from the nearness of two lone pairs on the focal chlorine molecule.
Fig. 4: V- shape of chlorite ion
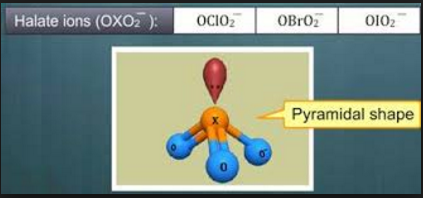
Halic acids, incorporates chloric acid, bromic acid and iodic acid. The halogen has the oxidation condition of +5 in these oxoacids. The individual halate particles are pyramidal shaped attributable to the nearness of a lone pair of electrons on the focal halogen atom.
Fig. 5: Pyramidal shape of halite ions
Perhalic acids, incorporates perchloric acid, perbromic acid and periodic acid. The oxidation condition of the halogen in these oxoacids is+7. The state of the perhalate particle is tetrahedral.
In any arrangement of oxoacids of halogens, the initial member has high acidic quality. This is because of the small size and high electro-negativity and little size of the particular halogens.
Example: Amongst perhalic acids, perchloric acid has high acidic quality. Since chlorine is more electro-negative than bromine or iodine, the shared electron pair lies moderately closer to chlorine in a Cl-O bond than bromine in a Br-O bond or iodine in an I-O bond. As an outcome, the O-H bond turns out to be much weaker if there should arise an occurrence of perchloric acid, along these lines encouraging the release of a proton promptly.
HOClO3 > HOBrO3 > HOIO3
Perchloric acid perbromic acid Periodic acid
The acidic quality of oxoacids increases with an expansion in the oxidation number of the halogen.
Example: Out of the four the four oxoacids of chlorine, the acidic quality increments especially from hypochlorous acid to perchloric acid
The strongest acid out of all the acids is the Perchloric acid.
Fig. 5: Acidic strength of halogen oxoacids series increases as we move down the group
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are oxoacids?
Sol. An oxoacid is an acid that contains oxygen. In particular, it is a compound that contains hydrogen, oxygen, and no less than one other element, with no less than one hydrogen molecule bound to oxygen that can separate to create the H+ cation and the anion of the acid.
Q2. What do all oxyacids have in common?
Sol. All oxyacids contain oxygen. In particular, it is a compound that contains hydrogen, oxygen, and no less than one other element, with no less than one hydrogen molecule bound to oxygen that can separate to create the H+ cation and the anion of the acid.
Q3. Do all acids contain hydrogen and oxygen?
Sol. By and large, oxoacids are basically polyatomic anions connected to hydrogen that is positive- polarized, which can be separated off as a cation. Under Lavoisier's unique hypothesis, all acids contained oxygen, which was named from the Greek ὀξύς (oxy: acid, sharp) and the root - γενής (- genes: creator). It was later found that a few acids, outstandingly hydrochloric acid, did not contain oxygen thus acids were partitioned into oxoacids and these new hydro acids.
Q4. Is hydrochloric acid an oxyacid?
Sol. No, as mentioned in the previous question it is a hydroacid.
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings