Beryllium
Table of Content |
Physical Properties of Beryllium
|
Property |
Value |
|
Density |
1.85 g/cm3 |
|
Melting point |
1560 K (1287°C, 4476°F) |
|
Boiling point |
2742 K (2469°C, 4476°F) |
|
Heat of fusion |
7.895 kJ/mol |
|
Heat of vaporization |
297 kJ/mol |
|
Heat capacity |
(25°C) 16.443 J/(mol/K) |
Refer to the follwoing video for the structure of beryllium atom
Anomalous Behaviour of Beryllium
Difference between beryllium and other alkaline earth metals
-
Beryllium is the lightest of all the alkaline earth metals.
-
It has higher melting and boiling points compared to other elements in group 2.
-
The oxides of beryllium, that is, BeO are amphoteric whereas other oxides of alkaline earth metals are strong bases.
-
Beryllium do not impart color during flame test.
-
Beryllium is small in size with high ionization enthalpy compared to other alkaline earth metals.
-
Beryllium do not form oxides similar to other alkaline earth metals.
-
Beryllium do not liberate hydrogen from acids as observed in other alkaline earth metals.
Some important points of difference between beryllium and magnesium are given below:
-
Be is harder than other members of its group.
-
Be is lighter than Mg.
-
Be does not react with water while Mg reacts with boiling water.
-
BeO is amphoteric while MgO is weakly basic.
-
Its melting and boiling points are higher than those of Mg & other members.
-
Be forms covalent compounds whereas other members form ionic compounds.
-
Beryllium carbide reacts with water to give methane whereas carbides of other alkaline earth metals gives acetylene gas.
Be2C + 4H2O → 2Be (OH)2 + CH4
Mg2C2 + 2H2O → Mg (OH)2 + C2H2
CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca (OH)2 + C2H2 -
Beryllium does not exhibit coordination number more than four as it has four orbitals in the valence shell. The other members of this group has coordination number 6.
Reason for the Anamolus Behaviour of Beryllium
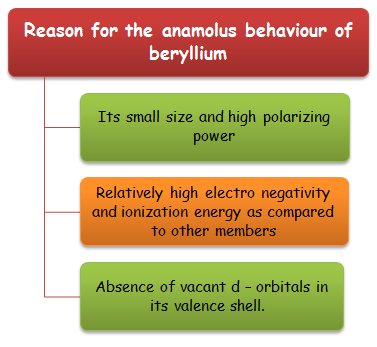 The properties of berrylium the first member of the alkaline earth metal, differ from the rest of the member. Its is mainly because of
The properties of berrylium the first member of the alkaline earth metal, differ from the rest of the member. Its is mainly because of
-
Its small size and high polarizing power.
-
Relatively high electro negativity and ionization energy as compared to other members.
-
Absence of vacant d – orbitals in its valence shell.
Resemblance of Beryllium with Aluminium (Diagonal Relationship)
The following points illustrate the anomalous behaviour of Be and its resemblance with Al.
-
Unlike groups – 2 elements but like aluminium, beryllium forms covalent compounds.
-
The hydroxides of Be, [Be(OH)2] and aluminium [Al(OH)3] are amphoteric in nature, whereas those of other elements of group – 2 are basic in nature.
-
The oxides of both Be and Al i.e. BeO and Al2O3 are high melting insoluble solids.
-
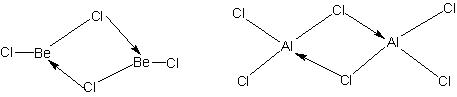
BeCl2 and AlCl3 have bridged chloride polymeric structure.
-
The salts of beryllium as well as aluminium are extensively hydrolysed.
-
Carbides of both the metal reacts with water liberating methane gas.
Be2C + 4H2O → 2Be (OH)2 + CH4
AI4C3 + 12H2O → 4Al (OH)3 + 3CH4 -
The oxides and hydroxides of both Be and Al are amphoteric and dissolve in sodium hydroxide as well as in hydrochloric acid.
BeO + 2HCl → BeCl2 + H2O
BeO + 2NaOH → Na2BeO2 + H2O
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + H2O -
Like Al, Be is not readily attacked by acids because of the presence of an oxide film.
Illustration: |
|
Question: Give the structure of BeCl2 in the
 |
Uses of Beryllium
-
Alloys of beryllium with copper or nickel are used for making gyroscopes, springs, electrical contacts, spot-welding electrodes and non-sparking tools.
-
Mixing beryllium with any metal to form alloy increases their electrical and thermal conductivity.
-
Some alloys of beryllium are used as structural materials for high-speed aircraft, missiles, and spacecraft and communication satellites also.
-
Beryllium is used in X –ray lithography also as it is transparent to X-rays

Question 1: Which of the following is not the correct reason for anomalous property of Be?
a. Its small size and high polarizing power.
b. Relatively high electro negativity and ionization energy as compared to other members.
c. Absence of vacant d – orbitals in its valence shell.
d. Presence of fully filled 2s orbital
Question 2: Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a. Be is harder than other members of its group.
b. Be is lighter than Mg.
c. Be does not react with water while Mg reacts with boiling water.
d. BeO is acidic while MgO is amphoteric.
Question 3: BeO + 2HCl →
a. BeCl2 + H2O
b. BeCl + H2O +Cl2
c. BeCl2 + Cl2
d. BeCl2 + H2
Question 4: Be is not readily attacked by acids because of the presence of
a. an oxide film
b. empty d orbitals
c. fully filled 2s orbital

|
Q.1 |
Q.2 |
Q.3 |
Q.4 |
|
d |
d |
a |
a |
Related Resources
-
Look here for past year papers of IIT JEE to get an idea about the type of questions asked in exam
-
You should also refer to the syllabus of chemistry for IIT JEE which would help you to plan your study
-
Knowing about the important books for preparing IIT JEE would help you alot.
To read more, Buy study materials of S- Block elements comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Chemistry here.
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More



2.jpg)