You won’t panic about learning animal kingdom after reading this as it is going to help you to crack AIPMT.
Most lively & beautiful life occurs among Kingdom Animalia. It is the most diversified kingdom among five kingdom system of classification given by R.H Whittaker. Let me tell you one thing, if you prepare this particular topic well, you have assured certain marks already. Still there is certain information about animal kingdom that you forgot to study. Don’t worry. What I am here for? Let’s discuss about animal kingdom today.
And yes! To make your learning better, you need to learn its classification first. After you learn the classification, you need to learn examples then. Then you can relate the characteristic of particular category with that organism. Now let’s study Animals 🙂
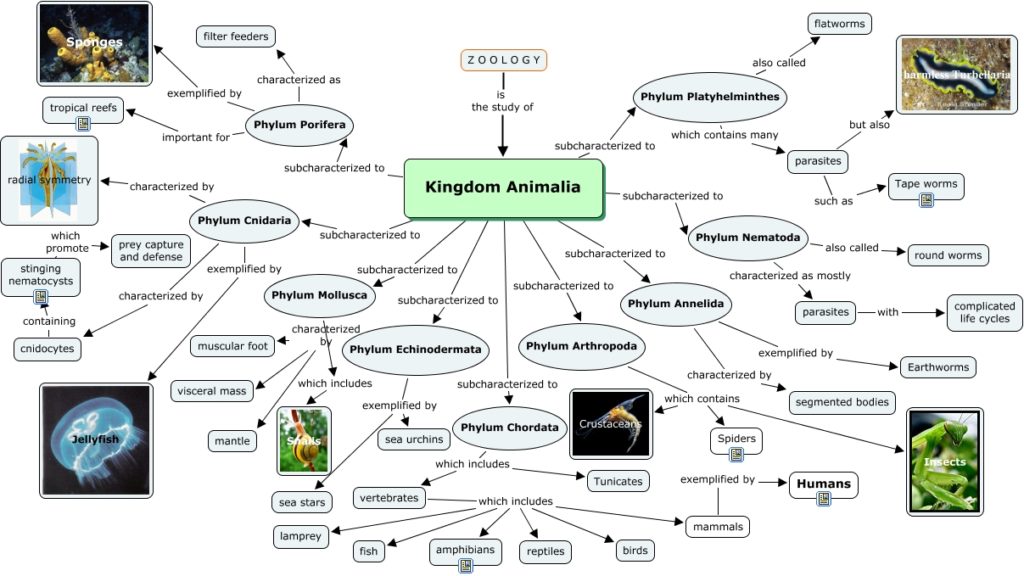
Give you 10 min to this picture. Look closely & learn about classification with characterization.
Still didn’t get it? Let me tell you one thing. The classification of any kingdom is done on the basis of certain characteristics. Same is done in animal kingdom. These features are:
- Level of organization – It include acellular, cellular. Tissue & organ level of complexity.
- Body Plan – It can be cell aggregate plan (E.g. sponges), blind sac plan (E.g. flatworms & cnidarians) & tube with in a tube plan (E.g. Mollucs, arthropods).
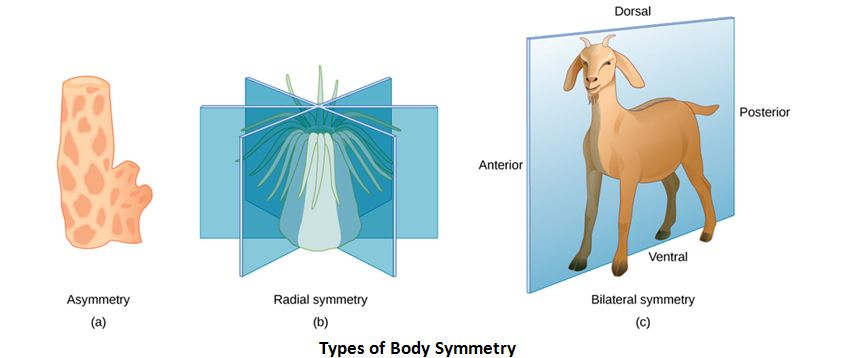
- Symmetry – Image says it all.
- Germ layers – Diploblastic (E.g. Porifera & cnidaria) organisms include ectoderm & endoderm only while triploblastic (E.g. Platyhelminthes) includes mesoderm as well.
- Coelom – On the basis of body cavity (coelom) organisms are acoelomates (E.g. sponges, flatworms), pseudo-coelomates (E.g. roundworms) & coelomates (or eucoelomates e.g. echinoderms, chordates).
- Mode of nutrition – Autotrophic & Heterotrophic
- Mode of respiration – Aerobic & anaerobic respiration.
- Types of eggs –
|
On the basis of quantity of yolk – |
|||
| Microlecithal | Very small amount of yolk. E.g. Egg of Herdmania, sea urchin etc. | ||
| Mesolecithal | Moderate amount of yolk. E.g. egg of frog, fish etc. | ||
| Macrolecithal | Large amount of yolk. E.g. egg of insects, shark etc. | ||
|
On the basis of yolk distribution – |
|||
| Homolecithal | Uniformly distributed yolk. E.g. egg of molluscs, protochordates etc. | ||
| Telolecithal | Yolk is concentrated in vegetal half. E.g. eggs of amphibians. | ||
| Meiolecithal | All ooplasm is covered by yolk. E.g. Egg of reptiles etc. | ||
| Centrolecithal | Yolk is centre localized. E.g. eggs of insects. | ||
- Mode of excretion – Refer to this link if you want to read detailed study about it 🙂
- Complexity of nervous system – It is from simple nerve cell to ganglia & then to whole complex nervous system. Then it includes Central & peripheral nervous system.
- Skeletal System – Exoskeleton & endoskeleton. It constitutes the framework of body.
- Endocrine system – Different organisms have different glands in their body. It forms the hormones in body.
- Presence of notochord – It is present in all chordates. Notochord is a type of solid flexible structure which is the derivative of mesoderm.
- Cleavage – It include indeterminate (Complete embryo is formed here after all blastomere stay altogether. E.g. chordates) & determinate type of cleavage (Blastomere separates in early stages here. E.g. annelids).
- Circulatory system – It is of two types viz. open (blood flow in open space. E.g. insects) & close type (blood flow in vessels. E.g. vertebrates).
Now you can move back that image & relate provided information.
This info is surely going to help you. If you want more information about this kingdom, just click the link here and if you are having any query right now. Why to wait? Just drop it over this link & it is going to be answered as soon as possible.
Let me mention myself too. I am Anjali Ahuja, one of the members of askIITians family. We always try our best to help you students in getting through the entrance exams. We have created study material for you guys. Click the link & get into the bank of knowledge 🙂
- Excited
- Fascinated
- Amused
- Bored
- Sad
- Angry