Education Options in India for Students from Middle East
 India has the second largest higher education network in the world. Here’s a bird-eye view of the Indian Education System:
India has the second largest higher education network in the world. Here’s a bird-eye view of the Indian Education System:
Universities in India
Set up by Central or State Governments only, they can be of following types:
- Central or State Universities: Central Universities are funded directly by the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) in India while State Universities are set up and funded by respective state governments.
- Deemed Universities: Major higher education institutions that enjoy the same academic status and privileges as a University are called Deemed Universities in India. These include the likes of Tata Institution of Social Sciences (TISS), Mumbai; the Deccan College of Post Graduate and Research Institute (DCPGRI), Pune; and Indian Institute of Sciences (IISc), Bengaluru.
- Institutions of National Importance: Some of the best and most prestigious institutions in India come under this category. Established by Acts of Indian Parliament, they are funded by the Central Government too. The Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) and the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) are all institutions of national importance.
Colleges in India
They have to seek affiliation to one of these Universities and can be set up either by the State Governments or by private bodies or trusts. The affiliating University decides the admission criteria and course syllabus for its colleges, holds exams, and awards degrees.
Colleges can be categorized into four categories depending on the courses they offer, who owns them, and how they are related to the University. They are:
- University Colleges: Owned and managed by universities, they are mostly situated in the campus of the University itself.
- Government Colleges: Very few, government colleges in India are only about 15 to 20% of the total number of colleges in the country. Like other colleges, they depend on the Universities they are affiliated to for all academic purposes.
- Privately Colleges: 70% of colleges in India are founded by Private Trusts or Societies. Regulated according to the University they are affiliated to, they are also funded by state governments.
- Professional Colleges: Engineering, Medical and Management colleges all come under this category.
There are about 1500 Vocational Colleges in India too that teach skills related to various industries to students. These colleges offer Certificate and Diploma level courses in various engineering trades as well as specific areas related to business, commerce, agriculture, paramedical, health, humanities and home science.
Courses in India
Most sought-after courses in India can be categorized under following disciplines:
- Courses in Agriculture, Dairy Technology, Fisheries or Veterinary Sciences,
- Courses in IT, Computer Sciences, Bio Informatics or Biotechnology,
- Engineering and Technology courses,
- Fashion Design & Technology courses,
- Medical, Dental, Nursing, Pharmacy or Paramedical courses,
- Miscellaneous Courses in Humanities, Commerce, Basic Sciences, Social Sciences, Management and Arts & Fine Arts, and
- Travel and Tourism as well as Hotel Management and Catering Technology courses.
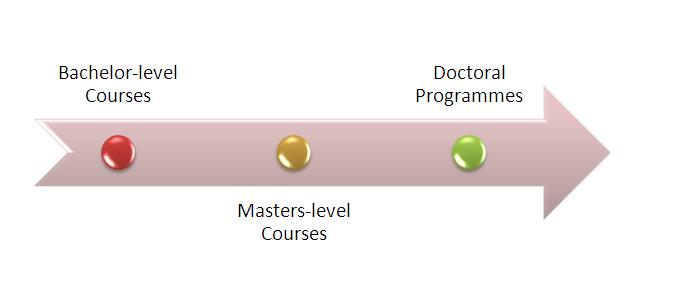
After 10+2, students can take admission to Degree programmes in India that are offered at following levels:
- Undergraduate Courses: Almost all the undergraduate courses in India are of three years and lead to Bachelors degree. The only exceptions are Engineering and Medical courses. Most of the undergraduate engineering programs have duration of four years while medical courses have duration of five and a half years. These programmes lead to Bachelor degrees.
- Postgraduate Courses:  Almost all postgraduate courses in India have duration of two years, including Master-level degree programmes in Engineering, Medicine, Business Administration, Arts and Science. In some rare cases, they can stretch up to three years if they include research work.
- Doctoral Courses: Doctoral courses in India include M.Phil and PhD programmes that involve research work under a guide, submitting a thesis and viva-voce. PhD course leads to the title of ‘Doctor’ in the chosen subject.
For some specialized fields like the Bachelor of Education (B.Ed) degree (meant for those who want to become Teachers), students must already have a Bachelor’s degree in any discipline beforehand.
Interested students may also look for certificate or diploma courses of shorter duration from universities in the fields of Engineering, Agricultural Sciences and Computer Technology.
askIITians offers professional online coaching classes to Gulf students and Middle East students to prepare for competitive entrance exams in India. These include Joint Entrance Exam (JEE) coaching programs for admission to engineering colleges, and All India Pre Medical Test (AIPMT) coaching programs for medical aspirants.
For any queries regarding education options in India or askIITians coaching programs, contact us at info@askIITians.com.
- Excited
- Fascinated
- Amused
- Bored
- Sad
- Angry