Revision Notes on Electrostatic
Electrostatic Force and Electrostatic field:- |
-
Electrostatic:- It is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.
- Coulomb’s Law:- It states that the electro-static force of attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies is directly proportional to the product of their charges and varies inversely as the square of the distance between the two bodies.
F = Kq1q2/r2
Here, K = 1/4πε0 = 9×109 Nm2C-2 (in free space)
- Relative Permittivity (εr):-
The relative permittivity (εr) of a medium is defined as the ratio between its permittivity of the medium (ε) and the permittivity (ε0) of the free space.
εr = ε/ε0
- Coulomb force in vector form:- The force on charge q1 due to q2 is,
![\vec{F_{12}} = [q_{1}q_{2}/r^{2}]\hat{r_{21}}](https://files.askiitians.com/cdn1/cms-content/common/latex.codecogs.comgif.latex_vecf_12q_1q_2r2_hatr_21.jpg)
If q1q2>0, R.H.S is positive.
If q1q2<0, a negative sign from q1q2 will change  and
and  . The relation will again be true, since, in that case have same directions.
. The relation will again be true, since, in that case have same directions.
- Unit of Charge:-
C.G.S, q = ±1 stat-coulomb
S.I, q = ±1 Coulomb
- Relation between coulomb and stat-coulomb:-
1 coulomb = 3×109 stat-coulomb
1 coulomb =(1/10) ab-coulomb (e.m.u of charge)
- Dielectric constant:- The dielectric constant (εr) of a medium can be defined as the ratio of the force between two charges separated by some distance apart in free space to the force between the same two charges separated by the same distance apart in that medium.
So, εr = ε/ε0 = F1/F2
Here, F1 and F2 are the magnitudes of the force between them in free space and in a medium respectively.
- Charges:-
? Line charge, λ = q/L
Surface charge, σ = q/A
Volume charge, ρ = q/V
- Electric field (
 ) :- The strength of an electric field is measured by the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point. The direction of field is given by the direction of motion of a unit positive charge if it were free to move.
) :- The strength of an electric field is measured by the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point. The direction of field is given by the direction of motion of a unit positive charge if it were free to move.

- Unit of Electric field:-
E = [Newton/Coulomb] or [Joule/(Coulomb) (meter)]
- Electric lines of force:- An electric line of force is defined as the path, straight or curved, along which a unit positive charge is urged to move when free to do so in an electric field. The direction of motion of unit positive charge gives the direction of line of force.

Properties:-
(a) The lines of force are directed away from a positively charged conductor and are directed towards a negatively charged conductor.
(b) A line of force starts from a positive charge and ends on a negative charge. This signifies line of force starts from higher potential and ends on lower potential.
- Electric field intensity due to a point charge:- E = (1/4πε0) (q/r2)
- Electric field Intensity due to a linear distribution of charge:-
 ?
?
(a) At point on its axis.
E = (λ/4πε0) [1/a – 1/a+L]
Here, λ is the linear charge density.
(b) At a point on the line perpendicular to one end.
?
Here λ is the line charge.
- Electric field due to ring of uniform charge distribution:-

At a point on its axis, E = (1/4πε0) [qx/(a2+x2)3/2]
- Electric field due to uniformly charged disc:-

Here σ is the surface charge.
- Electric field due to thin spherical shell:-
(a) Eout = (1/4πε0) (q/r2)
(b) Ein = 0

- Electric field of a non-conducting solid sphere having uniform volume distribution of charge:-

(a) Outside Point:- Eout = (1/4πε0) (Q/r2)
(b) Inside Point:- Ein = (1/4πε0) (Qr/R3)
(c) On the Surface:- Esurface = (1/4πε0) (Q/R2)
Here, Q is the total charge
- Electric field of a cylindrical conductor of infinite length having line charge λ:-

(a) Outside the cylinder:- E = λ/2πε0r
(b) Inside the cylinder:- E = 0
- Electric field of a non-conducting cylinder having uniform volume density of charge:-
(a) Outside the cylinder:- E = λ/2πε0r
(b) Inside a point:- E = ρr/2ε0
- Electric field of an infinite plane sheet of charge surface charge (σ) :- E = σ/2ε0

- Electric field due to two oppositely infinite charged sheets:-
(a) Electric field at points outside the charged sheets:-
EP = ER = 0
(b) Electric field at point in between the charged sheets:-
EQ = σ/ε0
- Electric Dipole:- An electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges situated very close to each other.
- Dipole Moment:- Dipole moment (
 ) of an electric dipole is defined as the product of the magnitude of one of the charges and the vector distance from negative to positive charge.
) of an electric dipole is defined as the product of the magnitude of one of the charges and the vector distance from negative to positive charge.

- Unit of Dipole Moment:- coulomb meter (S.I), stat coulomb cm (non S.I)
- Electric field due to an electric dipole:-
(a) At any point on the axial line:-

Alt Tag: Electric field due to an electric dipole on the axial line.

(b) At a point on the equatorial line (perpendicular bisector):-


(c) At any point:-


- Torque (
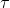 ) acting on a electric dipole in a uniform electric field (E):-
) acting on a electric dipole in a uniform electric field (E):-
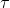 = pE sinθ
= pE sinθ
Here, p is the dipole moment and θ is the angle between direction of dipole moment and electric field E.
- Electric Flux:- Electric flux ?E for a surface placed in an electric field is the sum of dot product of
 and
and  for all the elementary areas constituting the surface.
for all the elementary areas constituting the surface.

- Gauss Theorem:- It states that, for any distribution of charges, the total electric flux linked with a closed surface is 1/ε0 times the total charge with in the surface.

- Electric field (E) of an infinite rod at a distance (r) from the line having linear charge density (λ):-
E = λ/2πε0r
The direction of electric field E is radially outward for a line of positive charge.
- Electric field of a spherically symmetric distribution of charge of Radius R:-

(a) Point at outside (r > R):- E = (1/4πε0) (q/r2), Here q is the total charge.
(b) Point at inside (r < R):- E = (1/4πε0) (qr/R3), Here q is the total charge.
- Electric field due to an infinite non-conducting flat sheet having charge σ:-
E = σ/2ε0

This signifies, the electric field near a charged sheet is independent of the distance of the point from the sheet and depends only upon its charge density and is directed normally to the sheet.
- Electric field due to an infinite flat conductor carrying charge:-
?E= σ/ε0
- Electric pressure (Pelec) on a charged conductor:-
Pelec = (½ε0) σ2
Electro-Static Potential and Capacitance:- |
- Electric Potential:-
(a) Electric potential, at any point, is defined as the negative line integral of electric field from infinity to that point along any path.

(b) V(r) = kq/r
(c) Potential difference, between any two points, in an electric field is defined as the work done in taking a unit positive charge from one point to the other against the electric field.
WAB = q [VA-VB]
So, V = [VA-VB] = W/q
Units:- volt (S.I), stat-volt (C.G.S)
Dimension:- [V] = [ML2T-3A-1]
Relation between volt and stat-volt:- 1 volt = (1/300) stat-volt
- Relation between electric field (E) and electric potential (V):-
E = -dV/dx = --dV/dr
- Potential due to a point charge:-
V = (1/4π ε0) (q/r)
- Potential at point due to several charges:-
V = (1/4π ε0) [q1/r1 + q2/r2 + q3/r3]
= V1+V2+ V2+….
- Potential due to charged spherical shell:-
(a) Outside, Vout = (1/4π ε0) (q/r)
(b) Inside, Vin = - (1/4π ε0) (q/R)
(c) On the surface, Vsurface = (1/4π ε0) (q/R)
- Potential due to a uniformly charged non-conducting sphere:-
(a) Outside, Vout = (1/4π ε0) (q/r)
(b) Inside, Vin = (1/4π ε0) [q(3R2-r2)/2R3]
(c) On the surface, Vsurface = (1/4π ε0) (q/R)
(d) In center, Vcenter = (3/2) [(1/4π ε0) (q/R)] = 3/2 [Vsurface]
- Common potential (two spheres joined by thin wire):-
(a) Common potential, V = (1/4π ε0) [(Q1+Q2)/(r1+r2)]
(b) q1 = r1(Q1+Q2)/(r1+r2) = r1Q/ r1+r2 ; q2 = r2Q/ r1+r2
(c) q1/q2 = r1/r2 or σ1/ σ2 = r1/r2
- Potential at any point due to an electric dipole:-
V (r,θ) = qa cosθ/4πε0r2 = p cosθ/4πε0r2
(a) Point lying on the axial line:- V = p/4πε0r2
(b) Point situated on equatorial lines:- V = 0
- If n drops coalesce to form one drop, then,
(a) R = n1/3r
(b) Q = nq
(c) V = n2/3Vsmall
(d) σ = n1/3 σsmall
(e) E = n1/3 Esmall
- Electric potential energy U or work done of the system W having charge q1 and q2:-
W = U = (1/4πε0) (q1q2/r12) = q1V1
- Electric potential energy U or work done of the system W of a three particle system having charge q1, q2 and q3:-
W = U = (1/4πε0) (q1q2/r12 + q1q3/r13 + q2q3/r23)
- Electric potential energy of an electric dipole in an electric field:- Potential energy of an electric dipole, in an electrostatic field, is defined as the work done in rotating the dipole from zero energy position to the desired position in the electric field.

(a) If θ = 90º, then W = 0
(b) If θ = 0º, then W = -pE
(c) If θ = 180º, then W = pE
- Kinetic energy of a charged particle moving through a potential difference:-
K. E = ½ mv2 = eV
-
Conductors:- Conductors are those substance through which electric charge easily.
-
Insulators:- Insulators (also called dielectrics) are those substances through which electric charge cannot pass easily.
-
Capacity:- The capacity of a conductor is defined as the ratio between the charge of the conductor to its potential
C = Q/V
Units:-
S.I – farad (coulomb/volt)
C.G.S – stat farad (stat-coulomb/stat-volt)
Dimension of C:- [M-1L-2T4A2]
- Capacity of an isolated spherical conductor:-
C = 4πε0r
-
Capacitor:- A capacitor or a condenser is an arrangement which provides a larger capacity in a smaller space.
-
Capacity of a parallel plate capacitor:-

Cair = ε0A/d
Cmed = Kε0A/d
Here, A is the common area of the two plates and d is the distance between the plates.
- Effect of dielectric on the capacitance of a capacitor:-
C = ε0A/[d-t+(t/K)]
Here d is the separation between the plates, t is the thickness of the dielectric slab A is the area and K is the dielectric constant of the material of the slab.
If the space is completely filled with dielectric medium (t=d), then,
C = ε0KA/ d
- Capacitance of a sphere:-
(a) Cair = 4πε0R
(b) Cmed = K (4πε0R)
- Capacity of a spherical condenser:-
(a) When outer sphere is earthed:-
Cair = 4πε0 [ab/(b-a)]
Cmed = 4πε0 [Kab/(b-a)]
(b) When the inner sphere is earthed:-
C1= 4πε0 [ab/(b-a)]
C2 = 4πε0b?
Net Capacity, C '=4πε0[b2/b-a]
Increase in capacity, ΔC = 4π ε0b
It signifies, by connecting the inner sphere to earth and charging the outer one we get an additional capacity equal to the capacity of outer sphere.
- Capacity of a cylindrical condenser:-
Cair = λl / [(λ/2π ε0) (loge b/a)] = [2π ε0l /(loge b/a) ]
Cmed = [2πKε0l /(loge b/a) ]
- Potential energy of a charged capacitor (Energy stored in a capacitor):-
W = ½ QV = ½ Q2/C = ½ CV2
- Energy density of a capacitor:-
U = ½ ε0E2 = ½ (σ2/ ε0)
This signifies the energy density of a capacitor is independent of the area of plates of distance between them so long the value of E does not change.
- Grouping of Capacitors:-
?(a)
(i) Capacitors in parallel:- C = C1+C2+C3+…..+Cn
 The resultant capacity of a number of capacitors, connected in parallel, is equal to the sum of their individual capacities.
The resultant capacity of a number of capacitors, connected in parallel, is equal to the sum of their individual capacities.
(ii)V1= V2= V3 = V
(iii) q1 =C1V, q2 = C2V, q3 = C3V
(iv) Energy Stored, U = U1+U2+U3
(b)
(i) Capacitors in Series:- 1/C = 1/C1 + 1/ C2 +……+ 1/Cn
 ?The reciprocal of the resultant capacity of a number of capacitors, connected in series, is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of their individual capacities.
?The reciprocal of the resultant capacity of a number of capacitors, connected in series, is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of their individual capacities.
(ii) q1 = q2 = q3 = q
(iii) V1= q/C1, V2= q/C2, V3= q/C3
(iv) Energy Stored, U = U1+U2+U3
- Energy stored in a group of capacitors:-
(a) Energy stored in a series combination of capacitors:-
W = ½ (q2/C1) + ½ (q2/C2) + ½ (q2/C3) = W1+W2+W3
Thus, net energy stored in the combination is equal to the sum of the energies stored in the component capacitors.
(b) Energy stored in a parallel combination of capacitors:-
W = ½ C1V 2 +½ C2V 2 + ½ C3V 2 = W1+W2+W3
The net energy stored in the combination is equal to sum of energies stored in the component capacitors.
- Force of attraction between plates of a charged capacitor:-
(a) F = ½ ε0E2A
(b) F = σ2A/2ε0
(c) F=Q2/2ε0A
- Force on a dielectric in a capacitor:-
F = (Q2/2C2) (dC/dx) = ½ V2 (dC/dx)
- Common potential when two capacitors are connected:-
V = [C1V1+ C2V2] / [C1+C2] = [Q1+Q2]/ [C1+C2]
- Charge transfer when two capacitors are connected:-
ΔQ = [C1C2/C1+C2] [V1-V2]
- Energy loss when two capacitors are connected:-
ΔU = ½ [C1C2/C1+C2] [V1-V2] 2
- Charging of a capacitor:-
(a) Q = Q0(1-e-t/RC)
(b) V = V0(1-e-t/RC)
(c) I = I0(1-e-t/RC)
(d) I0 = V0/R
- Discharging of a capacitor:-
(a) Q = Q0(e-t/RC)
(b) V = V0(e-t/RC)
(c) I = I0(e-t/RC)
- Time constant:-

Title:
Revision Notes on Electrostatic | askIITians
Meta description:
Revision Notes on electrostatic force, electrostatic field, electro static potential, electrostatic energy and capacitance provides by askIITians.
You Might Like to Refer:
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More
