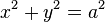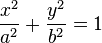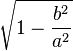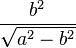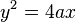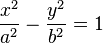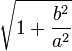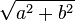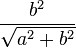SHAIK AASIF AHAMED
Last Activity: 11 Years ago
Hello student,
Aconic section(or justconic) is acurveobtained as the intersection of acone(more precisely, a right circularconical surface) with aplane. Inanalytic geometry, a conic may be defined as aplane algebraic curveof degree 2. There are a number of other geometric definitions possible. One of the most useful, in that it involves only the plane, is that a conic consists of those points whose distances to some point, called afocus, and some line, called adirectrix, are in a fixed ratio, called theeccentricity.
The three types of conics are theellipse,parabola, andhyperbola. Thecirclecan be considered as a fourth type (as it was by Apollonius) or as a kind of ellipse. Thecircleand theellipsearise when the intersection of cone and plane is aclosed curve. The circle is obtained when the cutting plane is parallel to the plane of the generating circle of the cone – for aright coneas in the picture at the top of the page this means that the cutting plane is perpendicular to the symmetry axis of the cone. If the cutting plane isparallelto exactly one generating line of the cone, then the conic is unbounded and is called a parabola. In the remaining case, the figure is a hyperbola. In this case, the plane will intersectbothhalves (nappes) of the cone, producing two separate unbounded curves.
| conic section |
equation |
eccentricity (e) |
linear eccentricity (c) |
semi-latus rectum (ℓ) |
focal parameter (p) |
| circle |
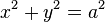 |
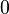 |
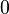 |
 |
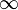 |
| ellipse |
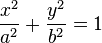 |
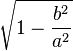 |
 |
 |
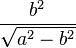 |
| parabola |
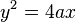 |
 |
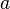 |
 |
 |
| hyperbola |
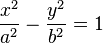 |
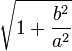 |
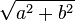 |
 |
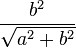
|
Thanks and Regards
Shaik Aasif
askIITians faculty