 8 grade science> State BOYLE”S LAW.
8 grade science> State BOYLE”S LAW.

 14 Answers
14 Answers
ash jai
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Raheema Javed
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
The statement of Boyle’s law is:
The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of gas remain unchanged within a closed system.
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
P directly proportional to 1/V
or
PV = k
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as
P1 V1 = P2 V2.
The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases.

Mohammed Anas
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Boyle's law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law is an experimental gas law which describes how the pressure of a gas tends to decrease as the volume of a gas increases. A modern statement of Boyle's law is:
The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of gasremain unchanged within a closed system.
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
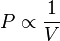
or
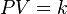
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Mohammed Anas
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Boyle's law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law is an experimental gas law which describes how the pressure of a gas tends to decrease as the volume of a gas increases. A modern statement of Boyle's law is:
The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of gasremain unchanged within a closed system.
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
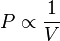
or
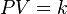
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Mohammed Anas
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Boyle's law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law∂ is an experimental gas law which describes how the pressure of a gas tends to decrease as the volume of a gas increases. A modern statement of Boyle's law is:
The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of gasremain unchanged within a closed system.
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
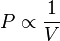
or
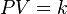
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
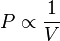
or
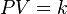
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
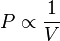
or
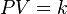
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
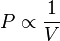
or
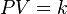
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
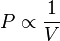
or
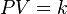
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
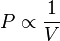
or
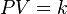
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
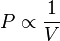
or
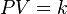
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
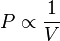
or
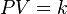
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
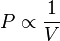
or
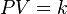
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.

Indranil Roy
Last Activity: 10 Years ago
Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as
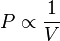
or
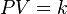
where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas, and k is a constant.
The equation states that product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of condition, the law can be usefully expressed as

The equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.
Provide a better Answer & Earn Cool Goodies

LIVE ONLINE CLASSES
Prepraring for the competition made easy just by live online class.

Full Live Access

Study Material

Live Doubts Solving

Daily Class Assignments
Ask a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free
Other Related Questions on 8 grade science

Which of the following is obtained form coal tar?
8 grade science
Last Activity: 2 Year ago(s)

Fill in the blanks : Different sound notes have different ……………… .
8 grade science
Last Activity: 2 Year ago(s)


कौन सा पदार्थ दहन के बाद गर्मी और प्रकाश देता है?
8 grade science
Last Activity: 2 Year ago(s)

Explain why tools meant for cutting and piercing always have sharp edges.
8 grade science
Last Activity: 2 Year ago(s)

