Human Physiology
Table of Content |
|
|
What is Human Physiology?
The study of function of human body is known as Human Physiology.
What does Physiologist do?
Physiologists are continually trying to answer questions related to the functions of single cells to Organs, Organ System, Organism and the interactions between Human Populations and Environment.
What is the definition of Physiological Disease?
Any disease caused due to change in physiology of some cell, tissue or organ is known as Physiological Disease. For Example: Diabetes, Hypertension, Cataract etc.
What is Medical Physiology all about?
The study of different systems of the human body from molecular level to organism level is known as Medical Physiology.
Levels of Organization
-
Molecule is composed of two or more atoms.
-
Macromolecules are large molecules and it includes carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
-
Cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
-
Cell organelles are small organs present in the cell. For Example: Nucleus, Mitochondria, Lysosomes, Golgi Apparatus etc.
-
Tissue is a group of cells that together form a particular function. For Example: Heart Tissue functions for relaxation and contraction of heart.
See Figure: Atom-molecule-organelle-cell-tissue-organ-organ system-organism
-
Organs are formed by combination of tissues such as Heart, Lungs, Kidneys etc.
-
Organ system consists of different organs working together. For Example : Cardiovascular System, Excretory System, Circulatory System etc.
Subdivisions of Human Physiology
-
Digestive system
-
Respiratory system
-
Excretory system
-
Nervous system
-
Endocrine system
Digestive System
This system comprises of different organs that work together in breakdown of complex food particles into simple food particles to obtain energy required for the survival of the individual.
The Human Digestive System includes a long digestive tract/alimentary canal and other accessory organs for digestion such as Liver, Pancreas, Salivary Glands etc.
Fig.2. Digestive system
Note: For detailed study of Digestive System, kindly refer to “Digestion and Absorption”.
Respiratory System
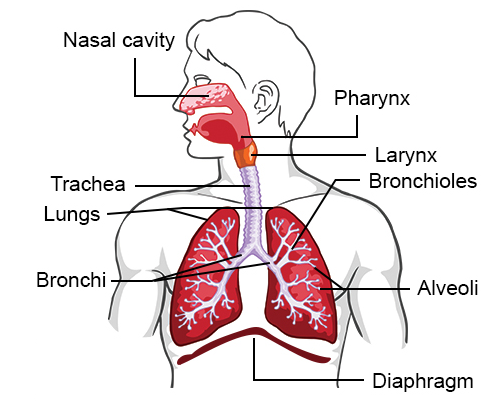
It is a system that helps in exchange of gases. It enables the person to respire. The main respiratory organ in humans is Lungs.
Fig.3. Respiratory System
Note: For detailed study of Respiratory System, kindly refer to “Breathing and Exchange of Gases”.
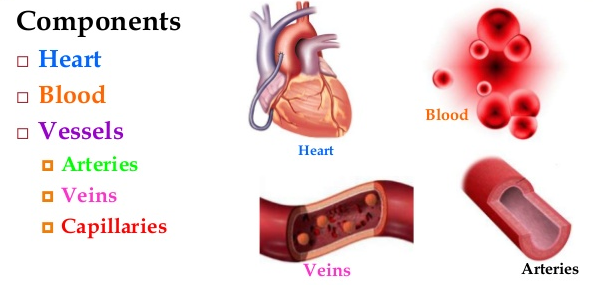
Circulatory System
It includes heart, blood, blood vessels, lymph and lymphatic system. This system helps in circulation of blood containing Oxygen, Nutrients, Hormones, Blood Cells, Carbon-Dioxide etc.
Fig.4. Components of Circulatory System
Note: For detailed study Circulatory System, kindly refer to “Body Fluids and Circulation”
Excretory System
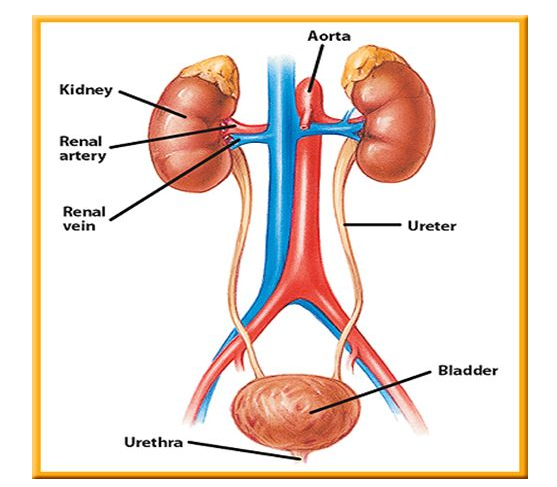
This system is meant to remove unwanted materials from the body in order to maintain homeostasis of the body and prevent damage to the body. The most important part of excretory system includes a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, single urinary bladder and a urethra. It also includes the accessory excretory organs like skin, Large Intestine, Liver, Lungs etc. The structural and the functional unit of kidney is known as Nephron. It helps in removal of nitrogenous waste from the body.
Fig.5. Excretory System
Note: For detailed study of Endocrine System, kindly refer to “Excretory Products and their Elimination”.
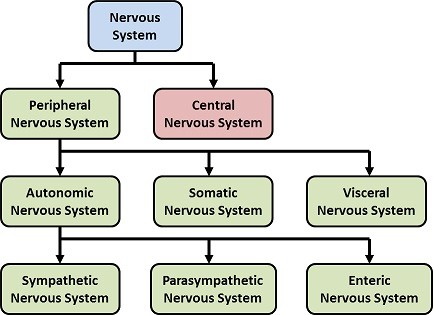
Nervous System
The Nervous System is a very important part of the animal body that coordinates Voluntary and Involuntary actions of the body. The structural and the functional unit of Nervous System is Neuron. The neuron or the nerve cells transmit information from one part of the body to another part of the body.
There are two types of nervous system in vertebrates:
Fig. 6. Components of Nervous System
Note: For detailed study of Nervous System, kindly refer to “Neural Control and Coordination”
Endocrine System
The Endocrine System consists of ductless glands that secretes chemical messengers known as Hormones that circulate in blood stream to reach different target organs. Glands that secrete hormones directly into bloodstream are known as Endocrine Glands.
Fig. 7. Endocrine Glands
Note: For detailed study of Endocrine System, kindly refer to the content “Chemical Control and Coordination”