Neural Control and Coordination
Table of Content |
 The Nervous System is a very important part of the animal body that coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions of the body.
The Nervous System is a very important part of the animal body that coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions of the body.
What is Nerve Impulse?
Any stimulus or signal that activate or inhibit any gland, muscle, organ, tissue or any nerve cell as known as Nerve impulse. For Example: When we touch a hot plate, a signal is transmitted to brain due to which we respond by removing our hand.
There are two types of Nervous System in vertebrates:
Fig.1. Divisions of Nervous System
What is Central Nervous System?
The central Nervous System comprises of Brain and the Spinal Cord.
Explain the Structure of Human Brain.
The Human Brain is covered by a membrane known as Meninges. Meninges are three in number. The Outermost Duramater, Middle Arachnoid and Innermost Piamater.
The longitudinal fissure divides the brain into two hemispheres known as Right Cerebral Hemisphere and Left Cerebral Hemisphere.
The Brain is divided into three parts: Forebrain, Midbrain and Hindbrain.
Forebrain
The Forebrain comprises of Cerebrum,Thalamus and Hypothalamus.
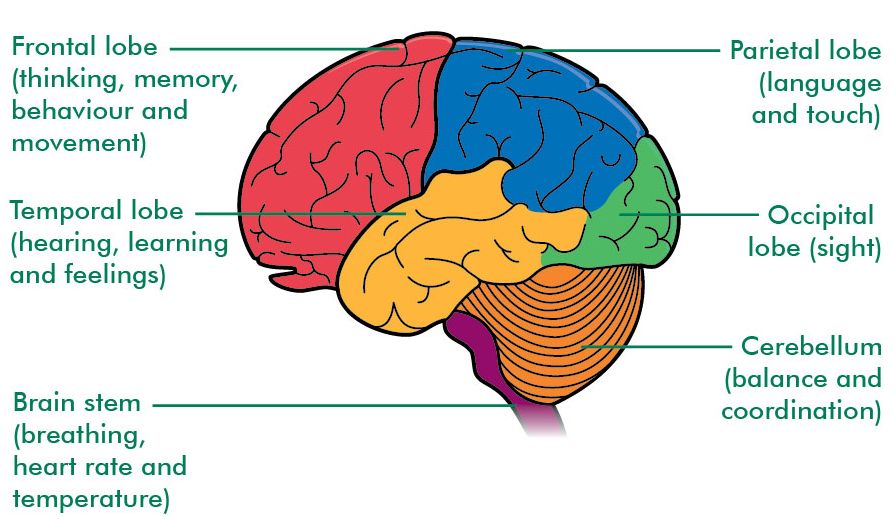
- Cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. It is divided into four lobes: Occipital Lobe, Parietal Lobe, Temporal Lobe and Frontal Lobe.
Fig.2. Different Lobes of Cerebrum and their function
Thalamus is olive shaped structure which performs sensory functions. It directs sensory input from the eyes, ears, tongue and from other sense organs.
Hypothalamus is located below the thalamus as the name suggests. It is important in monitoring hormone concentrations, water concentrations, temperature of the body etc.
Midbrain
It is a small part of the brain. It is associated with Vison, Hearing, Sleep, Arousal, Temperature etc.
Hindbrain
It consists of Cerebellum, Pons and Medulla Oblongata.
-
Cerebellum is involved in controlling attention, language, equilibrium, posture, etc.
-
Pons controls digestive and respiratory movements.
-
Medulla Oblongata connects skull with the spinal cord. It helps in controlling Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, Respiratory Movement, Vomiting etc.
What are Neurons/Nerve Cell?
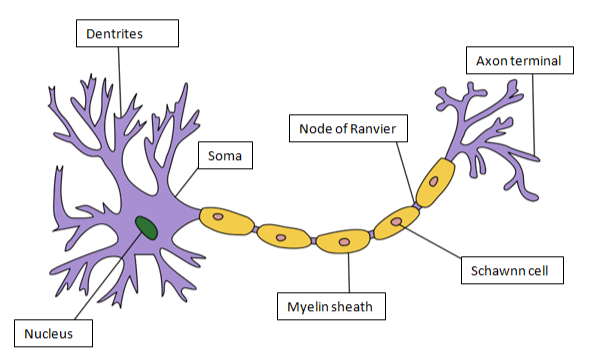
The structural and the functional unit of brain is Neuron. Neuron is divided into Cell Body, Axon and Dendrites. Cell body/soma of the neuron contain nucleus. It also contains Nissl Granules, composed of endoplasmic reticulum. Dendrites are branched projections from the cell body. Axon is a long, slender in shape that transmits nerve impulse from one neuron to another.
The cells found in axon are known as Schawnn Cell. Myelin sheath is schawnncells. Myelin sheath is an electrically insulating layer which is required for fast and efficient nerve impulse transmission. A gap between adjacent Schawnn Cells is known as Nodes of Ranvier.
Example of different types of Neurons
-
Sensory Neurons transmit nerve impulses from sensory receptors to central nervous system.
-
Motor Neurons transmit nerve impulses from central nervous system to muscle or a gland.
-
Inter Neurons connects different neurons within the brain and spinal cord.

Spinal Cord
It is a thin, tube-like structure which extends from the medulla of the brain to the lumbar region of vertebral column. It helps in transmission of nerve impulses from the brain to the rest of the body. It also coordinates reflex action.
There are 31 pairs of Spinal Nerves on each side of the vertebral column. These Spinal Nerves are grouped into:
-
8 pairs of cervical nerves
-
12 pairs of thoracic nerves
-
5 pairs of lumbar nerves
-
5 pairs of sacral nerves
-
One pair of coccygeal nerves
The Spinal Cord is made up of White Matter and Gray Matter. The butterfly shaped structure present at the center of the spinal cord is known as Gray Matter.
Fig.5. Structure of Spinal Cord
The region around the gray matter is known as White Matter. White matter contains nerves that are covered with Myelin Sheath whereas gray matter contains nerves without myelin sheath.
What is Reflex Action?
The involuntary response towards any stimulus is known as Reflex Action.
What is Reflex Arc?
The pathway of reflex action is known as Reflex Arc. Some sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain; they innervate in the spinal cord. This reduces the time of reflex action.
What is Peripheral Nervous System?
It consists of nerves and ganglia. Ganglia is a cluster of nerves. Peripheral Nervous System connects central nervous system to different organs and limbs.
Peripheral nervous system is divided into Autonomic Nervous System and Somatic Nervous System. Autonomic nervous system is associated with communication to internal organs and glands. Somatic nervous system communicates with sensory organs and voluntary muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System is further divided into Parasympathetic Nervous System and Sympathetic Nervous System.
Difference between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System
|
|
Sympathetic Nervous System |
Parasympathetic Nervous System |
|
Type of Control |
Involuntary |
Involuntary |
|
Number of neurons per message |
Two (Preganglionic shorter than Postganglionic) |
Two (Preganglionic longer than Postganglionic) |
|
Location of motor fiber |
Cranial (e.g., vagus) and sacral spinal nerves |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
Norepinephrine |
Acetylcholine |
|
Effectors |
Smooth and cardiac muscle, glands |
Human Sense Organs
Humans have five sense organs, They are: Eyes, Ears, Nose, Skin and Tongue.
The structure of Eye and Ear is explained below:
 Structure of the Eye
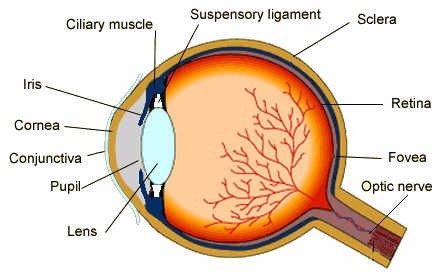
Structure of the Eye
Eye is a sense organ for sight. It consists of three layers: Outermost Sclera, Middle Choroid which is supplied with blood vessels and Inner Retina. The membrane that covers the sclera is known as Conjunctiva. Retina contains light sensitive cells known as Rods and Cones. Rods are cells that allow vision in dim light whereas cones help in color vision. Light enters the eye via cornea.
The nerve that connect eye to brain is known as Optic Nerve. Transparent lens focuses light on retina which helps in vision. The muscles that contracts and relaxes the lens is known as Suspensory Ligament. This is dependent on the amount of light that falls on the lens.
The colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters the eye is known as Pupil. Fovea is an exact location where light is focused on the retina.
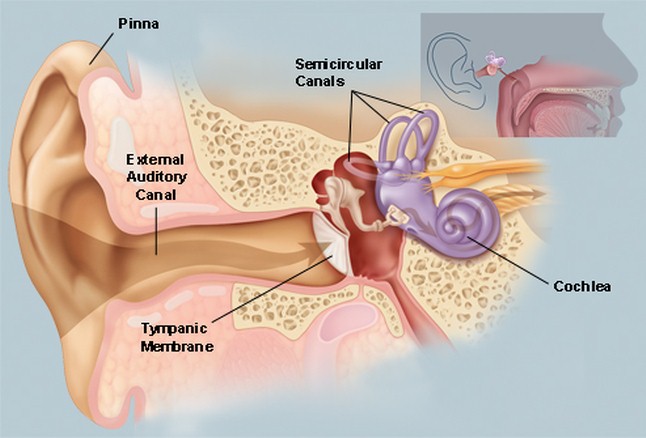
Structure of Ear
Ear is meant for hearing. The ear is divided into External Ear, Middle Ear and Inner Ear. The outer part of the ear is known as Ear Pinna. Ear pinna is covered by a membrane known as Tympanic Membrane.
When sound strikes the pinna it vibrates and vibrations are passed to cochlea which is a part of the inner ear. There are fluid-filled canals present that are attached to cochlea, are known as Semi-Circular Canals. These canals help in maintaining equilibrium or balance of the body.
Stimulus and Response
It is defined as any detectable change in the internal or the external environment. The ability of an organism to react against the stimulus is known as Response.
Synapse
The junction between the two Nerve cells is known as Synapse.
Second Brain in Humans
The Enteric Nervous System is known as Second Brain in Humans.
Saltatory Conduction
During Nerve Impulse transmission, the nerve impulse jumps over the Nodes of Ranvier. This mode of nerve impulse transmission is known as Salutatory Conduction. This is the fast mode of nerve impulse transmission.
Watch this Video for more reference
To read more, Buy study materials of Neural Control and Coordination comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Biology here