Magnification and Thin Lens
Table of Content |
Magnification
In new Cartesian sign convention, we define magnification is such a way that a negative sign (of m) implies inverted image and vice-versa. A real image is always inverted one and a virtual one is always erect. Keeping these points in mind and that the real object and its real image would lie on the same sides in case of mirror and on opposite sides in case of lenses.
 Let us consider an object OO ′ placed on the principal axis with its height perpendicular to the principal axis as shown in figure. The ray OP passing through the optic centre will go un deviated. The ray O ′A parallel to the principal axis must pass through the focus F2. The image is formed where O ′PI ′ and AF2I ′ intersect. Draw a perpendicular from I ′ to the principal axis. This perpendicular II ′ is the image of OO ′.
Let us consider an object OO ′ placed on the principal axis with its height perpendicular to the principal axis as shown in figure. The ray OP passing through the optic centre will go un deviated. The ray O ′A parallel to the principal axis must pass through the focus F2. The image is formed where O ′PI ′ and AF2I ′ intersect. Draw a perpendicular from I ′ to the principal axis. This perpendicular II ′ is the image of OO ′.
The linear or transverse magnification is defined as the ratio of the size of the image to that of the object.
Thus, Magnification m = Size of the image/Size of the object = II'/OO' = h2/h1
Here h1 is the height of the object and h2 is the height of the image. From the similar right angled triangles OO′P and II ′P, we have,
II'/OO' = PI/PO
II' = – h2 OO' = +h1
PI = +v PO = – u
Substituting this in the above equation, we get magnification
m = –h2/ +h1 = +v/-u
So,

The magnification is negative for real image and positive for virtual image. In the case of a concave lens, it is always positive.
Using lens formula the equation for magnification can also be obtained as,
m = h2/h1 = v/u = (f – v) / f = f/f+u
This equation is valid for both convex and concave lenses and for real and virtual images.
Power of a Lens
 Power of a lens is a measure of the degree of convergence or divergence of light falling on it. The power of a lens (P) is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length.
Power of a lens is a measure of the degree of convergence or divergence of light falling on it. The power of a lens (P) is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length.

The unit of power is dioptre (D) : 1 D = 1 m-1. The power of the lens is said to be 1 dioptre if the focal length of the lens is 1 meter. P is positive for converging lens and negative for diverging lens. Thus, when an optician prescribes a corrective lens of power + 0.5 D, the required lens is a convex lens of focal length + 2 m. A power of -2.0 D means a concave lens of focal length -0.5 m.
Thin Lens
A lens is a transparent medium (usually glass) bounded by two curved surfaces (generally either spherical, cylindrical, or plane surfaces). As illustrated in figure the line which passes normally through both bounding surfaces of a lens is called the optic axis. The point O on the optic axis which lies midway between the two bounding surfaces is called the optic centre.
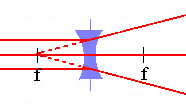 There are two basic kinds of lenses: converging, and diverging. A converging lens brings all incident light-rays parallel to its optic axis together at a point F, behind the lens, called thefocal point, or focus, of the lens. A diverging lens spreads out all incident light-rays parallel to its optic axis so that they appear to diverge from a virtual focal point F in front of the lens. Here, the front side of the lens is conventionally defined to be the side from which the light is incident. The differing effects of a converging and a diverging lens on incident light-rays parallel to the optic axis (i.e., emanating from a distant object) are illustrated in figure.
There are two basic kinds of lenses: converging, and diverging. A converging lens brings all incident light-rays parallel to its optic axis together at a point F, behind the lens, called thefocal point, or focus, of the lens. A diverging lens spreads out all incident light-rays parallel to its optic axis so that they appear to diverge from a virtual focal point F in front of the lens. Here, the front side of the lens is conventionally defined to be the side from which the light is incident. The differing effects of a converging and a diverging lens on incident light-rays parallel to the optic axis (i.e., emanating from a distant object) are illustrated in figure.
Image formation in Thin Lenses
-
A ray entering a converging lens parallel to its axis passes through the focal point F of the lens on the other side.
-
A ray entering a diverging lens parallel to its axis seems to come from the focal point F.
-
A ray passing through the center of either a converging or a diverging lens does not change direction.
-
A ray entering a converging lens through its focal point exits parallel to its axis.
-
A ray that enters a diverging lens by heading toward the focal point on the opposite side exits parallel to the axis.
Combination of Thin Lenses in contact
Let us consider two lenses A and B of focal length f1 and f2 placed in contact with each other. An object is placed at O beyond the focus of the first lens A on the common principal axis. The lens A produces an image at I1. This image I1 acts as the object for the second lens B. The final image is produced at I as shown in figure. Since the lenses are thin, a common optical centre P is chosen.
Let PO = u, object distance for the first lens (A), PI = v, final image distance and PI1 = v1, image distance for the first lens (A) and also object distance for second lens (B).
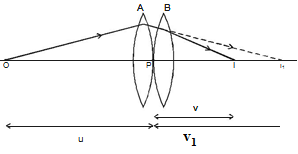 For the image I1 produced by the first lens A,
For the image I1 produced by the first lens A,
1/v1 – 1/u = 1/f1 ….... (1)
For the final image I, produced by the second lens B,
1/v – 1/v1 = 1/f2 …... (2)
Adding equations (1) and (2),
1/v – 1/u = 1/f1 + 1/f2 …... (3)
If the combination is replaced by a single lens of focal length F such that it forms the image of O at the same position I, then
1/v – 1/u = 1/F …... (4)
From equations (3) and (4),
1/F = 1/f1 + 1/f2 …... (5)
This F is the focal length of the equivalent lens for the combination.
 The derivation can be extended for several thin lenses of focal lengths f1, f2, f3 ... in contact. The effective focal length of the combination is given by,
The derivation can be extended for several thin lenses of focal lengths f1, f2, f3 ... in contact. The effective focal length of the combination is given by,
 …... (6)
…... (6)
In terms of power, equation (6) can be written as,
 …... (7)
…... (7)
The power of a combination of lenses in contact is the algebraic sum of the powers of individual lenses.
Watch this Video for more reference
|
|
Problem (JEE Main):
A concave mirror has a focal length 20 cm. The distance between the two positions of the object for which the image size is double of the object size is
(a) 20 cm (b) 40 cm
(c) 30 cm (d) 60 cm
Solution:
For real image, u = – u1, v = – 2u1 and f = – 20 cm
Substituting in 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
We get,
(1/-2u1) – (1/u1) = – 1/20
Or, u1 = 30 cm
For virtual image, u = – u2, v = 2u2, f = – 20 cm
So, 1/2u2 – 1/u2 = – 1/20
Or, u2 = -10 cm
The distance between two positions of the object are u1 – u2.
So, u1 – u2 = 30 cm – 10 cm = 20 cm
Thus from the above observation we conclude that, option (a) is correct.


Question 1
A converging lens is used to form an image on a screen. When the lower half of the lens is covered by an opaque screen then,
(a) half of the image will disappear
(b) complete image will be formed
(c) no image is formed
(d) intensity of the image is high
Light passes through a closed tube which contains a gas. If the gas inside the tube is gradually pumped out, the speed of light inside the tube
(a) increases (b) decreases
(c) remains constant (d) first increases and then decreases
A positive magnification greater than unity indicates _____________________.
(a) real image (b) virtual image
(c) neither real not virtual image (d) distorted image
Which of the following is a true statement?
(a) The power of a lens is always positive.
(b) The power of a lens is always negative.
(c) The power of a convex lens is positive.
(d) The power of a concave lens is positive.
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object.The position of the object should be ________.
(a) beyond the center of curvature of mirror
(b) between the center of curvature and the focus
(c) at the center of curvature of the mirror


| Q.1 | Q.2 | Q.3 | Q.4 | Q.5 |
|
b |
a |
b |
c |
c |
Related Resources
-
You might like to diffraction.
-
For getting an idea of the type of questions asked, refer the Previous Year Question Papers.
-
Click here to refer the most Useful Books of Physics.
-
To get answer to any question related to magnification and thin lens click here.
To read more, Buy study materials of Ray Optics and Optical Instruments comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Physics here.



