Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis
Table of Content |
 The relationship between the quantity of electric charge passed through an electrolyte and the amount of the substance deposited at the electrodes was presented by Faraday in 1834, in the form of laws of electrolysis.
The relationship between the quantity of electric charge passed through an electrolyte and the amount of the substance deposited at the electrodes was presented by Faraday in 1834, in the form of laws of electrolysis.
Faraday’s First Law
This law states that “the mass of a substance deposited or liberated at any electrode is directly proportional to the amount of charge passed” i.e., w a q (where w is the mass of the substance deposited or liberated and q is the amount of charge passed). This proportionality can be made into an equality by, w = zq
where z is the proportionality constant called the electrochemical equivalent. It is the mass of the substance in grams deposited or liberated by passing one coulomb of charge.
Faraday’s Second Law
This law states that “the mass of a substance deposited or liberated at any electrode on passing a certain amount of charge is directly proportional to its chemical equivalent weight”.
That is w a E where w is the mass of the substance in grams while E is its chemical equivalent weight in gms per equivalent =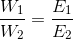 .
.
This law can be explained as follows.
Consider three reactions, such as:
Na+ + e– → Na
Cu2+ + 2e–- → Cu
Al3+ + 3e– → Al
Assume that these three reactions are occurring in three separate electrolytic cells connected in series.
.png) When x moles of electrons are passed through the three cells, the mass of Na, Cu and Al deposited are 23x gms, 31.75x gms and 9x gms respectively.
When x moles of electrons are passed through the three cells, the mass of Na, Cu and Al deposited are 23x gms, 31.75x gms and 9x gms respectively.
We can see that 23, 31.75 and 9 gm/eq are the chemical equivalent weights of the three elements.
w = moles of electrons 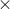 E
E
The charge possessed by 1 mole of electrons
= 1.6 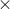 10–19
10–19 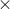 6.023 x 1023 ≈ 96500 C
6.023 x 1023 ≈ 96500 C
This charge is called as 1 Faraday.
If we pass one Faraday of charge, it means that we are passing one mole of electron and by passing 1 Faraday of charge 1gm equivalent weight of the substance will be deposited or liberated.
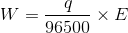
By combining the first and second law, we get
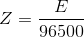
Note:It should be made clear that the cathode is the electrode in which reduction reaction(s) occurs while the anode is the electrode where the oxidation reaction(s) occurs. Do not relate the sign (positive or negative) of the electrode with the nature of the electrode. |
Coulomb is the unit of electric charge. It is the amount of charge that moves past may given point in a circuit when a current of 1 ampere is supplied for one second.
|
|
|
|

Question 1: Which of the following equations represent Faraday’s 1st law of electrolysis?
a. w= zq
b. 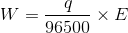
c. 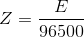
d. 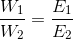
Question 2: The charge possessed by 1 mole of electrons =
a. 1 F
b. 1 C
c. 96500 C
d. 96500 F
Question 3: 1 Faraday = .
a.92365 C
b.96500 C
c.92100 C
d.99500 C
Question 4: Which of the following equations is the combination of first and second law of electrolysis?
a. w= zq
b. 
c. 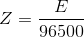

|
Q.1 |
Q.2 |
Q.3 |
Q.4 |
|
a |
c |
b |
c |
Related Resources
-
Click here to get the Syllabus of IIT JEE Chemistry
-
Look into the Sample Papers for an idea about type of questions asked in IIT JEE.
-
You can look for Useful Books of Chemistry
-
You can also refer to Electrode Potential
To read more, Buy study materials of Electrochemistry comprising study notes, revision notes, video lectures, previous year solved questions etc. Also browse for more study materials on Chemistry here.
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More





