Environmental Pollution
Table of Content |
What is Environment Pollution?
The undesirable changes in the surroundings are known as environment pollution. Changes in the environment affects the plants, animals as well as human beings. Any substance that causes pollution is known as pollutant. Pollutant can be solid, liquid or gas. Pollutant can be released into the environment via natural process or man-made activities.
Types of Pollutants
Pollutants can be degradable, such as discarded vegetables. On the other hand, pollutants can be non-biodegradable which remains in the environment for long time. Such as, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), plastic materials, heavy metals, etc. In plants, sulphur dioxide causes flower buds to fall from the plant. Hydrocarbons are carcinogenic in nature. Excessive use of fossil fuels causes atmospheric pollution
Atmospheric Pollution
Atmosphere has different layers or regions in which it is divided -
-
Troposphere is the lowest region where living organisms including human beings inhabit.
-
Stratosphere is the layer above troposphere where ozone is present. Ozone prevents the ultraviolet rays from reaching the earth.
-
Mesosphere is where the temperature is low. The air is thin to breathe.
-
Thermosphere is the layer where rays from the atmosphere are first absorbed such as X-rays, UV-rays etc.
Types of Environment Pollution
Following are the types of pollution that effect our environment:
Tropospheric Pollution
It occurs when some solid or gaseous particles are suspended in air.
Fig. 2. Tropospheric Pollution
Pollutants are divided into gaseous air pollutants and particulate pollutants.
Fig. 3. Common Pollutants
Gaseous Air Pollutants
-
Oxides of Sulphur are formed when fossil fuels are burnt. The most common end product of burning of fossil fuel is Sulphur dioxide. Even a very low concentration of Sulphur dioxide is harmful for plants and animals and causes, respiratory disorders. Not only this, it causes irritation in eyes such as tears and redness. In plants, Sulphur dioxide causes flower buds to fall from the plant. These oxides have potential for acid rain. The reactions are follows:
2SO2 (g) +O2 (g) → 2SO3(g)
SO2 (g) +O3 (g) → SO3(g) + O2 (g)
SO2 (g) + H2O2(l) → H2SO4(aq)
-
Oxides of nitrogen are formed when lightning strikes the oxygen at higher altitude. During burning of fossil fuels at high temperature, oxygen and nitrogen combines to form nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide.
N2 + O2 → 2NO
Nitric oxide than reacts further with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide.
2NO +O2 → 2NO2
NO formed also reacts with ozone to from nitrogen dioxide and oxygen. High concentration of nitrogen dioxide causes damage to plant leaves. It causes lung irritant. It also causes respiratory problems.
-
Hydrocarbons are composed of hydrogen and carbon. They are carcinogenic, that is, they are agents that causes cancer. They cause ageing in plants, shedding of flowers and leaves etc.
-
Oxides of carbon includes carbon monoxide and carbon-dioxide. Carbon monoxide is one of the toxic pollutant. Carbon monoxide has a strong affinity to bind with hemoglobin. This reduces the amount of oxygen that bind the hemoglobin. This forms carboxyhemoglobin which causes reduce availability of oxygen to tissues. Incomplete combustion of carbon, automobile exhaust contains carbon-dioxide. As number of vehicles are increasing with increasing population, the concentration of carbon monoxide is increasing in the atmosphere.
Fig. 4. Common pollutants and their effects
Carbon dioxide is added to the atmosphere by respiration, burning of fossil fuels, and decomposition of limestone. Released carbon-dioxide is taken in by plants during photosynthesis to balance the carbon-dioxide released in the atmosphere. But as deforestation is increasing, the rate of carbon-dioxide taken in by plants decreases. The effects of increased carbon-dioxide in atmosphere is Global warming and Green- house effect.
Global Warming
Most of the energy released by the sun is retained by the atmosphere which raises the temperature. The rest of the heat radiates back to the atmosphere. This heat is trapped by gases, for example, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, chlorofluorocarbon compounds (CFCs) and water vapor present in the atmosphere. This raises the temperature of the atmosphere, this is known as Global Warming.
Fig. 5. Global Warming
Green-house effect occurs when flowers, vegetables and fruits are grown in glass covered areas. Glass has the capability to capture energy from the sun and prevents the heat to reflect in the atmosphere. This increases the temperature in the green house. This is known as green-house effect. This is observed in cold places. The solar radiations heat up the plants and soil. Green-house gases includes carbon-dioxide, water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, CFCs, and the ozone.
Acid Rain
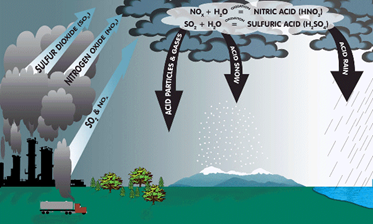 Precipitation containing acidic components such as sulfuric or nitric acid in dry or wet form. Precipitation can be in the form of rain, snow, fog, dust, or hail etc. Normally rain water has pH of 5.6. When pH falls below 5.6, it is known as acid rain. The main cause of acid rain is human activities such as burning of coal, oil in power stations, furnaces, burning of petrol and diesel etc.
Precipitation containing acidic components such as sulfuric or nitric acid in dry or wet form. Precipitation can be in the form of rain, snow, fog, dust, or hail etc. Normally rain water has pH of 5.6. When pH falls below 5.6, it is known as acid rain. The main cause of acid rain is human activities such as burning of coal, oil in power stations, furnaces, burning of petrol and diesel etc.
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) + 2H2O (l) → 2H2SO4 (aq)
4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)+ 2H2O (l) → 4HNO3 (aq)
Acid rain is harmful for agriculture, trees and plants. Acid rain washes away the nutrients that are required for the growth of the plants. It causes respiratory problems in human beings and animals. When it reaches the aquatic system, it affects plants and animal life in aquatic system.
Acid rain damages buildings made up of stone or metal. The Taj Mahal in India is the most important example of damage by acid rain. This is due to presence of industries in area where Taj Mahal is located. The acid rain reacts with marble (CaCO3) of Taj Mahal.
CaCO3 +H2SO4 → CaSO4 + H2O+ CO2
Fig. 7. Acid Rain
Particulate Pollutants
It includes minute solid particles or liquid droplets suspended in air. The source of particulate pollutants can be smoke particles from fires, vehicle emissions, ash, dust particles etc. Bacteria, viruses, moulds, algae also act as particulate pollutant.
Classification of non-viable particulate pollutants are as follows -
-
Smoke particulates formed during combustion of organic matter. For example, garbage, burning of fossil fuels, smoke from burning of oil.
-
Dust are particles that are formed due to various sources such as crushing or grinding of solid particles. Sand, saw dust, fly ash, etc. are also important source of particulate matter.
-
Mists are small water droplets that decreases the visibility in the atmosphere. For example, Mist from herbicide and insecticides.
-
Fumes are another non-viable particulate pollutants that are formed due to condensation of vapors during distillation, boiling etc.
Smog
Combination of smoke and fog forms smog. There are two types of smog-
-
Classical smog is a mixture of smoke, Sulphur dioxide and fog. It occurs in cool and humid environment.
-
Photochemical smog is a combination of formaldehyde, acrolein, nitric oxide, ozone, and PAN. It occurs in warm and sunny environment.
Formation of Photochemical Smog
During the burning of fossil fuels, a large variety of pollutants are released into the environment. The main pollutants released during burning includes hydrocarbons and nitric oxide. When the concentration of these pollutants increases to a certain level, a chain of reaction occurs with sunlight to form nitrogen dioxide
NO2(g) → NO(g) + O(g)
When nitrogen dioxide absorbs energy, it breaks down into nitric oxide and oxygen atom. Oxygen atom is highly reactive, so it combines with oxygen to form ozone.
O(g) + O2 (g) → O3 (g)
Ozone combines with nitric oxide to form nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
NO (g) + O3 (g) → NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Ozone is toxic and is a strong reducing agent which can react with unburnt hydrocarbons to produce 3 products- acrolein, peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and formaldehyde.
Effects of Photochemical Smog
-
Causes eye irritation
-
Damage to the plant life.
-
Corrosion of stones and metals.
-
It also leads to cracking in rubber.
Stratospheric Pollution
Stratosphere contains ozone layer that protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays. Th wavelength of these harmful ultraviolet radiation is 255 nm. These ultraviolet radiations cause skin cancer in humans. Oxygen when absorbs ultraviolet rays, it breaks into oxygen atoms. These oxygen atoms when combine with oxygen, they form ozone.
But nowadays there are reports which suggest that ozone layer is getting depleted by certain pollutants. The main pollutant behind the ozone depletion is chlorofluorocarbon (CFCs) known as Freon. CFCs are used in refrigerators. These CFCs in atmosphere absorbs ultraviolet rays and forms chlorine free radical.
CF2Cl2 (g) → Chlorine° (g) + C° F2Cl (g)
The chlorine radical reacts with ozone to form chlorine monoxide and molecular oxygen.
Cl° (g) + O3 (g) → ClO° (g) + O2(g)
Chlorine monoxide than reacts with oxygen atom to produce chlorine free radical.
ClO°(g) + O° (g) → Cl° (g) + O2 (g)
These chlorine free radicals formed are continuously used to breakdown the ozone.
Ozone Hole
During 1980s scientists, had reported that there is depletion of ozone in the Antarctica region, this is known as ozone hole. During summer time, nitrogen dioxide and methane combines with chlorine monoxide and chlorine atoms forming chlorine sinks and thus prevents ozone depletion. But during winter season, polar stratospheric clouds are formed over Antarctica. These are special clouds that provide a surface for chlorine nitrate formation. These clouds then get hydrolyzed to form hypochlorous acid. Hypochlorous acid the combines with hydrogen chloride to form molecular chlorine.
Steps of Ozone Hole formation
Control of Air Pollution
-
Automobiles should be designed in such a way that they emit least pollutants.
-
Use of smoke free furnaces.
-
Railway steam engine should be avoided.
-
Industries should be set up away from the residential areas.
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More