Periodic Classification of Elements
There are total of 118 element6 known so far and the discovery of new elements still continues. Every element has its own importance in the environment , some of them are useful while other are harmful. The harmful elements may also be useful in other way.
It becomes a necessity to study the chemical and physical properties of each of the elements present around us because every element is related to our life in some or other way. As the number is very large and there is possibility that more elements will be discovered, so it becomes very difficult to study each of them separately. We need to classify them in some groups according to their properties so that we can study them in group more easily and effectively. Periodic table is the tool which is used to classify the known elements in groups.
It helps us to undertake a systematic study of the various elements found in nature without which it would have been impossible for us to study all the elements in the table. With the help of periodic table a comparative study of the elements and their compounds can be done.
Periodic table also helps us to analyse the periodic trend in various properties such as ionisation potential, electron affinity, electronegativity etc.
Dobereiner's Triads, 1829
Dobereiner was the first scientist to classify the elements in some groups.
He tried to classify the elements with similar properties in groups of three elements (Triads). He could succeed in making only a few triads.
In the triads of elements the atomic weight of the middle element was the arithmetic mean of the atomic weights of the other two. Some of the triads are as under
|
Li |
Na |
K |
Ca |
Sr |
Ba |
P |
As |
Sb |
Cl |
Br |
I |
|
7 |
23 |
39 |
40 |
88 |
137 |
31 |
75 |
120 |
35.5 |
80 |
123 |
Newland's Law of Octaves, 1864
If the elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic weights, every eighth element had similar properties to the first one like the first and eighth note in music. For example
|
sa |
re |
ga |
ma |
pa |
dha |
ni |
sa |
|
Li |
Be |
B |
C |
N |
O |
F |
Na |
|
Na |
Mg |
Al |
Si |
P |
S |
Cl |
K |
The main problem with this classification was that inert gases were not discovered at that time and also all the elements could not be classified on this basis.
Mendeleef’s Periodic Table
Mendeleef’s Periodic law : The physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic weights.
If the elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic weights, after a regular interval elements with similar properties are repeated
On the basis of his law, Mendeleef proposed a periodic table for classicication of elements which is known as Mendeleef’s Periodic Table
The table is divided into nine vertical columns called groups and seven horizontal rows called periods.
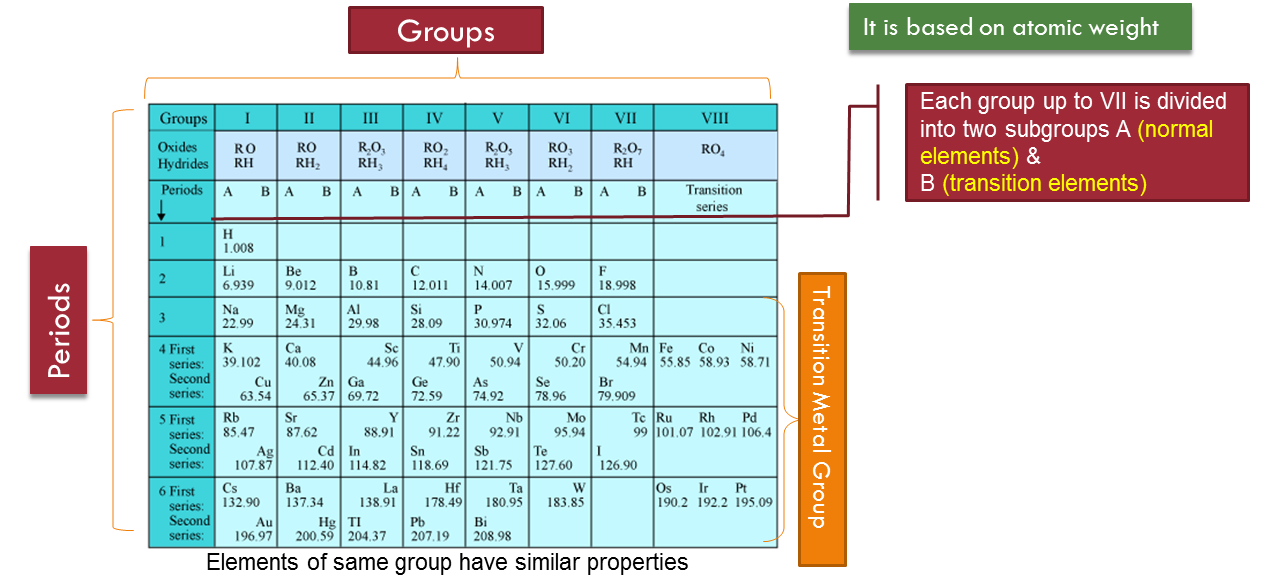
Merits or Advantages of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
-
Study of Elements: First time all known elements were classified in a group according to their similar properties. So, study of the properties of elements become easier.
-
Predicting new Elements: It gave encouragement to the discovery of new elements as some gaps were left in it. Sc, Ge, Tc were the elements for whom position and properties were defined by Mendeleev even before their discoveries and he left the blank spaces for them in hit table.
Blank space at atomic weight 72 in Si group was called Eka silicon and element discovered later was named Germanium.-
Eka Aluminium: Gallium
-
Eka Boron: Scandium
-
Eka Manganese: Technetium
-
Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
-
Position of Hydrogen: Hydrogen resembles both, the alkali metals (1A) and halogens(VII A) in properties so Mendeleev could not decide where to place it.
-
Position of Isotopes: As atomic weight of isotopes differ, they should have been placed in different position in Mendeleev’s periodic table. But there were no such positions for isotopes in Mendeleev’s periodic table
-
Anomalous Pairs of Elements: There were some pair of elements which did not follow the increasing order of atomic weights. E.g: Ar and Co were placed before K and Ni respectively in the table but having higher atomic weights.
-
Like Elements were Placed in Different Groups: Pt and Ag which have similar properties were placed in group VIII and group IB respectively.
-
Position of Isotopes: As atomic weight of isotopes differ, they should have been placed in different position in Mendeleev’s periodic table. But there were no such positions for isotopes in Mendeleev’s periodic table
-
Anomalous Pairs of Elements: There were some pair of elements which did not follow the increasing order of atomic weights. E.g.: Ar and Co were placed before K and Ni respectively in the table but having higher atomic weights.
Refer to the following video for Modern Periodic Table
We will gain in depth knowledge of this chapter under following subtopics:
Modern Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Law: Properties of elements are the periodic function to their atomic numbers.
-
The periodicity in properties is due to repetition of similar outer shell electronic configuration at a certain regular intervals.
-
In modern periodic table is based on modern periodic law in which elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers.
-
In the modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in rows and columns. These rows and columns are known as periods and groups respectively.
-
The table consists of 7 periods and 18 groups
-
Period indicates the value of ‘n’ (principal quantum number) for the outermost or valence shell.
-
Same number of electrons is present in the outer orbitals (that is, similar valence shell electronic configuration

Characteristics of Periods
-
First period is called shortest period and contains only two elements. Second and third periods are called short periods containing eight elements each. Fourth and fifth periods are long periods containing eighteen elements each. Sixth period is the longest period with thirty-two elements. Seventh period is an incomplete period containing nineteen elements. Numbers 2, 8,8,18,18, 32 are called magic numbers.
-
Lanthanide and actinide series containing 14 elements each are placed separately under the main periodic table. These are related to sixth and seventh periods of III group respectively.
-
Elements of third period from sodium (Na) to Chlorine (Cl) are called representative or typical elements.
-
Valency of an element in a period increases from 1 to 7 with respect to oxygen.
Na2O
MgO
Al2O3
SiO2
P2O5
SO3
Cl2O7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-
From left to right in a period generally
-
Atomic weight, effective nuclear charge, ionisation potential, electronegativity and electron affinity of an element increases.
-
Atomic radius, electropositive character and metallic character of an element decreases.
-
-
Diagonal relationship — Elements of second period Li, Be and B resemble closely with the elements Mg, Al and Si of third period in the next higher group.
Second Period Li Be B C
Third Period Na Mg Al Si
- Elements of second period are called bridge elements.
Characteristic of Groups
-
There are nine groups in modern periodic table and they are represented by roman numerals as I, II, III, IV, V, Vi, VII, VIII and zero.
-
Groups I to VII are further divided into two subgroups A and B, Group VIII consists of three sets, each one containing three elements.
-
Inert gases or noble gases are placed in zero group.
-
The valency of an element in a group is equal to the group number.
-
The elements of the groups which resemble the typical elements are called normal elements. For example IA, IIA, IIIA, IVA, VA, VIA, VIIA group elements are normal elements.
-
Those elements of the groups which do not resemble the typical elements are called transition elements. For example- IB, IIB, IIIB, IVB, VB, VIB, VIIB, and VIII group elements are transition elements.Hydrogen is placed in both IA and VIIA groups.
-
Atomic weight, atomic size, electropositive character and metallic character of elements increases down the group.
-
Ionisation potential, electron affinity and electronegativity of elements decreases down the group.
Classification of Elements

On the basis of electronic configuration, the elements may be divided into four groups.
s-block elements
- These are the elements in which last electron enters s subshell.
-
These are present in the left part of the periodic table.
-
These include 1 and 2 group elements.
-
All the s- block elements are metals.
-
The general electronic configuration of valence shell for s block elements is ns1-2 ( n = 1 to 7).
p – block elements
-
These are the elements in which last electron enters p subshell.
-
These are present in the right part of the periodic table.
-
These include 13 to 18 of the periodic table.
-
Most of the p block elements are metalloids and non metals but some of them are metals also.
-
The general electronic configuration of the valence shell is ns2np1-6 ( n = 2 to 7).
-
ns2 np6 is stable noble gas configuration. The electronic configuration of He is Is2.
d-Block Elements
-
These are the elements in which last electron enters d-subshell.
-
These are present in the middle part of the periodic table (between s & p block elements)
-
d block elements include group 3 to 12 groups of the periodic table.
-
All are d block elements are metals.
-
The last electrons fills in ( n – 1)d orbital.
-
The outermost electronic configuration of d block elements is (n-1)d1-10 ns1-2 (n = 4 to 7).
-
There are three series of d-block elements as under
- 3d series – Sc(21) to Zn (30)
- 4d series – Y (39) to Cd (48)
- 5d series – La (57), Hf (72) to Hg (80)
f -Block Elements
-
These are placed separately below the main periodic table.
-
These are mainly related to IIIB i.e. group 3 of the periodic table
-
There are two series of f-block elements as under
-
4f series – Lanthanides – 14 Elements i.e. Ce (58) to Lu (71)
-
5 f series – Actinides – 14 Elements i.e. Th (90) to Lw (103)
-
the last electron fills in ( n – 2) ¦-orbital
-
Their general outermost electronic configuration is (n-2)¦1-14 (n-1)s2 (n-1)p6 (n-1)d0-1ns2 (n = 6 and 7).
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Related Resources
Click here to get acess to the coordination compounds
Click to download the past year papers of IIT JEE
You can also download the NCERT text books for free.
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More
