Extraction of Crude Metal from Concentrated Ore
Table of Content |
What is Crude Metal?
The ore is considered as crude metal. It is a solid mass from which pure metal can be obtained.
Steps for Extraction of Metal
Extraction of metals involves three major steps:
-
Isolation of metal from the concentrated Ore
-
Purification of the metal
Isolation of metal from the concentrated Ore involves the refining of metals from the compounds. The first step is to convert an ore into an oxide. Then the oxide is reduced using a reducing agent.
Conversion to Oxide- Metal refining is done by heating the ore in a limited supply or absence of oxygen. For example, hydrated ferric oxide is heated to form dry ferric oxide.
Fe2O3.xH2O(s) → Fe2O3 (s) + xH2O(g)
Fig. 1. Equation of conversion ore to oxide
Roasting- During this process, extraction is done by heating the ore in a regular supply of air. Sulphide ores of elements such as Zinc, Lead and Copper are treated and concentrated using this methodology. The sulphur in the ore, at high temperature reacts with the oxygen to form Sulphur Dioxide and escapes out.
2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2
Fig. 2. Roasting
Reduction of Oxide to Metal – It is a process of removal of oxygen. Generally, reducing agents such as carbon or carbon monoxide is used in this step. Carbon is added to the metal oxide obtained from the ore and then heated.
MxOy + yC → xM + y CO
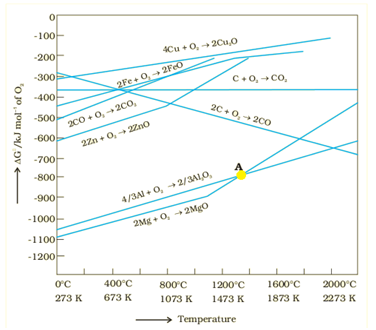
Ellingham Diagram
It is a graphical representation of Gibbs energy. These diagrams are used for finding the choice of reducing agent in the reduction of the oxides. These are used to find out the feasibility of thermal reduction of an ore.
Limitations of Ellingham Diagram
-
It does not give any information regarding the kinetics of the reduction process.
-
These diagrams believe that reactants and products are in equilibrium, but this is not always the case.
Calcination
The process of heating in limited supply or absence of air is known as calcination.
Examples of calcination processes include the following:
-
decomposition of carbonate minerals, as in the calcination of limestone to drive off carbon dioxide;
-
decomposition of hydrated minerals, as in the calcination of bauxite and gypsum, to remove crystalline water as water vapor;
-
decomposition of volatile matter contained in raw petroleum coke;
Watch this Video for more reference
More Readings
View courses by askIITians


Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals
Click Here Know More

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts
Click Here Know More

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child
Click Here Know More

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Click Here Know MoreAsk a Doubt
Get your questions answered by the expert for free