The chemistry of the triiodomethane (iodoform) reaction
What the triiodomethane (iodoform) reaction shows
A positive result - the pale yellow precipitate of triiodomethane (iodoform) - is given by an aldehyde or ketone containing the grouping:
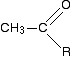
"R" can be a hydrogen atom or a hydrocarbon group (for example, an alkyl group).
If "R" is hydrogen, then you have the aldehyde ethanal, CH3CHO.
-
Ethanal is the only aldehyde to give the triiodomethane (iodoform) reaction.
-
If "R"is a hydrocarbon group, then you have a ketone. Lots of ketones give this reaction, but those that do all have a methyl group on one side of the carbon-oxygen double bond. These are known as methyl ketones.
Equations for the triiodomethane (iodoform) reaction
We will take the reagents as being iodine and sodium hydroxide solution.
The first stage involves substitution of all three hydrogens in the methyl group by iodine atoms. The presence of hydroxide ions is important for the reaction to happen - they take part in the mechanism for the reaction (not required for UK A level).

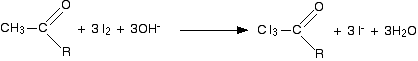
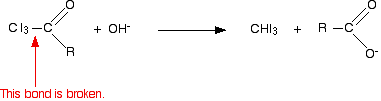
In the second stage, the bond between the C I3 and the rest of the molecule is broken to produce triiodomethane (iodoform) and the salt of an acid.

Putting all this together gives the overall equation for the reaction:

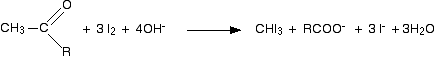
please hit if u like



