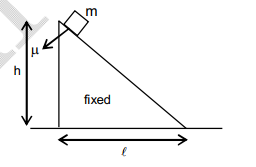
To determine the speed of a block sliding down an inclined plane when it reaches the bottom, we can apply principles from physics, particularly those related to energy conservation and kinematics. Although I can't see the image you mentioned, I can guide you through the general process of solving this type of problem.
Understanding the Forces at Play
When a block is placed on an inclined plane, several forces act on it. The primary forces include:
- Gravitational Force (Weight): This force acts downward and can be broken into two components: one perpendicular to the incline and one parallel to it.
- Normal Force: This force acts perpendicular to the surface of the incline and balances the perpendicular component of the gravitational force.
- Frictional Force: If the surface is not frictionless, this force opposes the motion of the block.
Energy Conservation Approach
One effective way to find the speed of the block at the bottom of the incline is to use the principle of conservation of energy. The potential energy (PE) at the top of the incline is converted into kinetic energy (KE) as the block slides down.
The potential energy at the top can be calculated using the formula:
PE = mgh
Where:
- m: mass of the block
- g: acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²)
- h: height of the incline
As the block slides down, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, which is given by:
KE = 0.5mv²
Where:
- v: final speed of the block
Setting Up the Equation
At the top of the incline, all energy is potential, and at the bottom, all energy is kinetic (assuming no energy is lost to friction). Thus, we can set the potential energy equal to the kinetic energy:
mgh = 0.5mv²
Notice that the mass (m) cancels out from both sides of the equation, simplifying our calculation:
gh = 0.5v²
Solving for Speed
Now, we can solve for the speed (v) of the block:
v² = 2gh
v = √(2gh)
This equation tells us that the speed of the block when it reaches the bottom of the incline depends on the height (h) from which it started and the acceleration due to gravity (g).
Example Calculation
Let’s say the height of the incline is 5 meters. Plugging in the values:
g = 9.81 m/s²
h = 5 m
Now, substituting these values into the speed equation:
v = √(2 * 9.81 * 5)
v = √(98.1)
v ≈ 9.9 m/s
This means that the block would reach the bottom of the incline at a speed of approximately 9.9 m/s, assuming no friction is acting on it.
Final Thoughts
By understanding the relationship between potential energy and kinetic energy, you can effectively analyze the motion of objects on inclined planes. If you have specific values or conditions from the image, feel free to share them, and we can work through the calculation together!