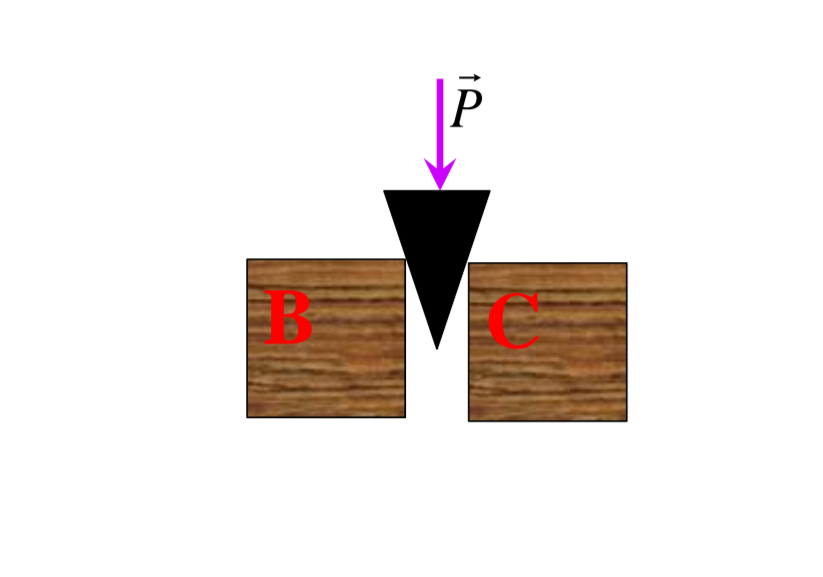
To determine the minimum force required to start moving the wedge between two blocks, we need to analyze the forces acting on the system. The problem involves two scenarios: one where both blocks B and C can move freely, and another where block C is fixed. Let's break this down step by step.
Understanding the Forces at Play
In both scenarios, the wedge will create a force that acts on the blocks due to its inclined surface. The friction between the blocks and the surface will play a crucial role in determining the force needed to start moving the wedge.
Given Data
- Height of the wedge (h) = 4 inches
- Base width of the wedge (b) = 1.5 inches
- Weight of each block (W) = 100 lbs
- Coefficient of friction (u) = 0.35
Scenario (a): Both Blocks Free to Move
When both blocks B and C are free to move, we need to consider the forces acting on the wedge and the blocks. The wedge will exert a force on block B, which in turn will affect block C. The frictional force that resists the motion of the blocks can be calculated as follows:
The normal force (N) acting on block B due to the wedge can be determined by the geometry of the wedge. The angle of the wedge can be found using the height and base width:
Using trigonometry, we find the angle θ:
tan(θ) = height/base width = 4/1.5
θ = arctan(4/1.5) ≈ 69.44 degrees
The normal force on block B (N_B) due to the wedge can be expressed as:
N_B = W_B * cos(θ) = 100 * cos(69.44)
The frictional force (F_friction) opposing the motion of block B is:
F_friction = u * N_B = 0.35 * N_B
To find the minimum force (P) required to start moving the wedge, we set up the equilibrium equations. The force P must overcome the frictional force acting on block B:
P = F_friction
After calculating the values, we find:
P = 0.35 * (100 * cos(69.44))
Scenario (b): Block C Fixed
In this case, block C is fixed to the horizontal surface, which changes the dynamics of the system. The wedge will still exert a force on block B, but now block C will not move, meaning the frictional force acting on block C must also be considered.
The normal force on block C (N_C) is equal to the weight of block C, which is 100 lbs. The frictional force opposing the motion of block C is:
F_friction_C = u * N_C = 0.35 * 100 = 35 lbs
For the wedge to start moving, the force P must overcome the total frictional force acting on both blocks. Therefore, we have:
P = F_friction_B + F_friction_C
Substituting the values, we find:
P = 0.35 * (100 * cos(69.44)) + 35
Final Thoughts
By calculating the forces in both scenarios, we can determine the minimum force required to start moving the wedge. The key takeaway is that the frictional forces at play significantly influence the amount of force needed, and fixing one of the blocks changes the dynamics of the system. Understanding these principles can help in analyzing similar problems in physics and engineering.