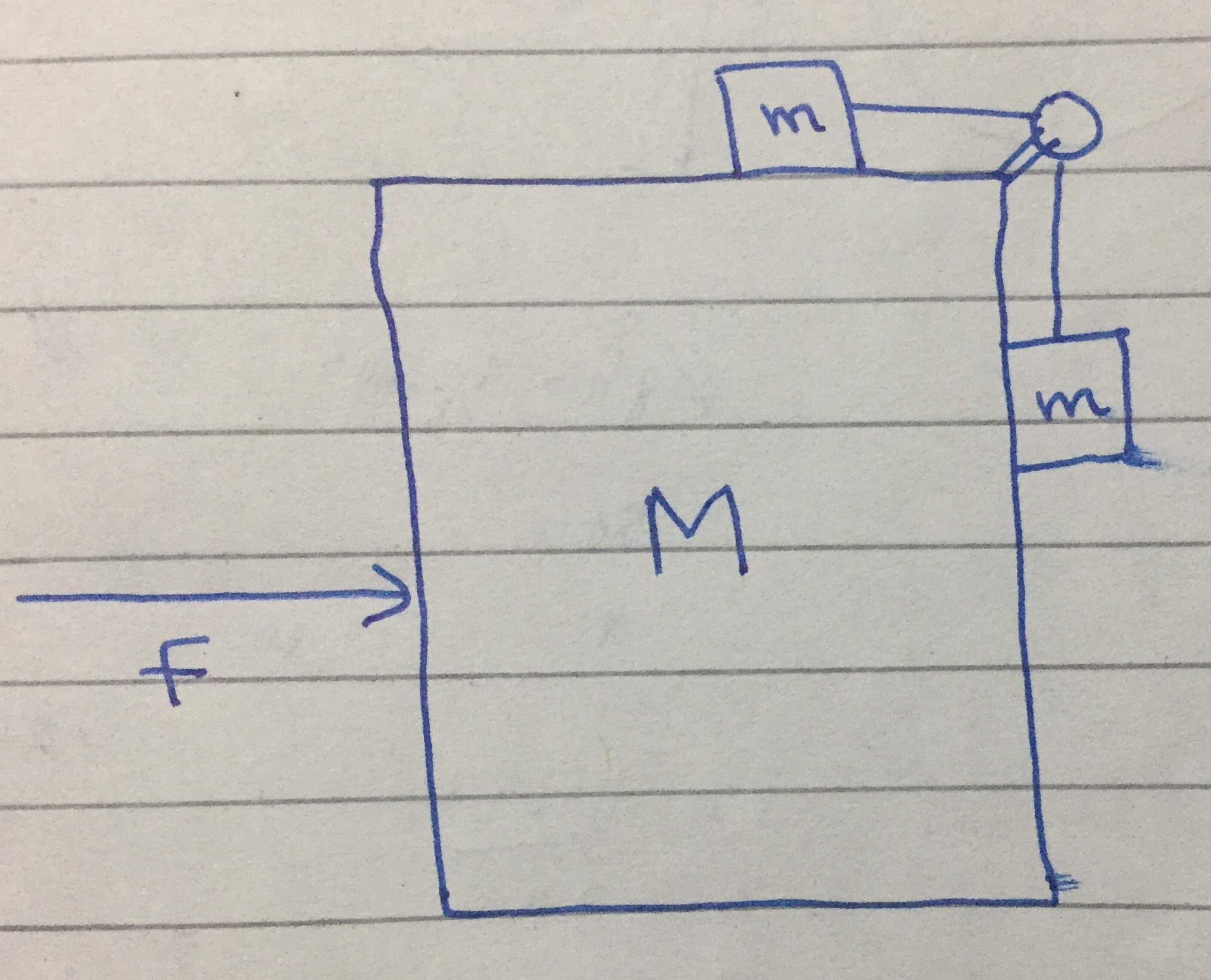
To determine the maximum and minimum forces that can be applied to a larger block without causing a smaller block to slip on top of it, we need to consider the forces acting on both blocks and the friction between them. This scenario typically involves understanding static friction, which prevents the smaller block from sliding off the larger one.
Understanding the Forces at Play
Let's break down the problem step by step. Assume we have two blocks: a larger block (Block A) and a smaller block (Block B) resting on top of it. The forces acting on Block B include gravitational force and the frictional force between the two blocks. The applied force on Block A will influence the frictional force that keeps Block B from slipping.
Key Variables
- m1: Mass of Block A (larger block)
- m2: Mass of Block B (smaller block)
- g: Acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²)
- μ: Coefficient of static friction between the two blocks
- F: Applied force on Block A
Calculating the Forces
The gravitational force acting on Block B can be calculated as:
Weight of Block B (W2) = m2 * g
The maximum static frictional force that can act on Block B before it starts to slip is given by:
Frictional Force (F_friction) = μ * W2 = μ * (m2 * g)
For Block B to remain stationary on Block A, the net force acting on it must not exceed this frictional force. When a force F is applied to Block A, it creates an acceleration (a) that affects both blocks. The relationship between the applied force, the frictional force, and the acceleration can be expressed as:
F - F_friction = (m1 + m2) * a
Finding Maximum Force
To find the maximum force (F_max) that can be applied without causing Block B to slip, we set the frictional force equal to the net force acting on Block B:
F_max = F_friction + (m1 + m2) * a
However, for Block B to just start slipping, we consider the scenario where the frictional force is at its maximum:
F_max = μ * (m2 * g) + (m1 + m2) * a
Finding Minimum Force
The minimum force (F_min) that can be applied while still keeping Block B from slipping occurs when the applied force is just enough to balance the frictional force:
F_min = (m1 + m2) * a - μ * (m2 * g)
Example Calculation
Let’s say:
- m1 = 5 kg (mass of Block A)
- m2 = 2 kg (mass of Block B)
- μ = 0.4 (coefficient of static friction)
- g = 9.81 m/s²
First, calculate the weight of Block B:
W2 = m2 * g = 2 kg * 9.81 m/s² = 19.62 N
Next, calculate the maximum frictional force:
F_friction = μ * W2 = 0.4 * 19.62 N = 7.848 N
Assuming we want to keep the blocks stationary (a = 0), the maximum force applied to Block A would be:
F_max = F_friction = 7.848 N
For the minimum force, if we consider a slight acceleration, we would need to adjust the calculations based on the desired acceleration.
Final Thoughts
In summary, the maximum and minimum forces that can be applied to the larger block without causing the smaller block to slip depend on the masses of the blocks, the coefficient of friction, and the acceleration. By understanding these relationships, you can effectively analyze similar problems in physics.