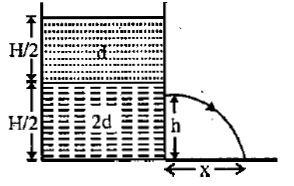
. (a) (i)
KEY CONCEPT:
Since the cylinder is in equilibrium in the liquid therefore Weight of cylinder = upthrust
mg =
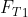
+
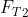
where
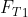
and
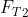
= upthrust due to lower and upper liquid respectively
A / 5 x L x D x g = A / 5 x L / 4 x 2d x g + A / 5 x 3L / 4 x d x g
⇒ D = 2d / 4 + 3d / 4 = 5d / 4
(ii) Total pressure at the bottom of the cylinder = Atmospheric pressure + Pressure due to liquid of density d + Pressure due to liquid of density 2d + Pressure due to cylinder [Weight /Area]
P = P0 + H / 2 dg + H / 2 x 2d x g + A/5 x L x D x g / A
P = P0 + (3H / 2 + L / 4)dg [∵ D = 5d/4]
(b) KEY CONCEPT :
Applying Bernoulli’s theorem
P0 + [H / 2 x d x g + (H / 2 - h) 2d x g ]
= P0 + ½ (2d)v2
⇒ v = √(3 H – 4h) / 4 g
Horizontal Distance x
Ux = v; t = t; x = vt ….(i)
For vertical motion of liquid falling from hole
uy = 0, Sy = h, ay = g, ty =t
S = ut + ½ at2
⇒ h = ½ gt2 ⇒ t = √2h / g … (ii)
From (i) and (ii)
x = vy x √2h /g = √(3H- 4H) g/2 x √2h/g
= √(3H – 4h)h ….(iii)
For finding the value of h for which x is maximum, we differentiate equation (iii) w.r.t. t
dx / dt = ½ [ 3 H – 4h)h]-1/2 {3H – 8h}
Putting dx/ dt = 0 for finding values h for maxima /minima
½ [ (3H – 4h )]-1/2 [3H – 8h] = 0
⇒ h = 3 H / 8
∴ xm = √[3H – 4 (3H / 8)] 3H/8
= √12H / 8 x 3H / 8 = 6H/ 8 = 3H/ 4