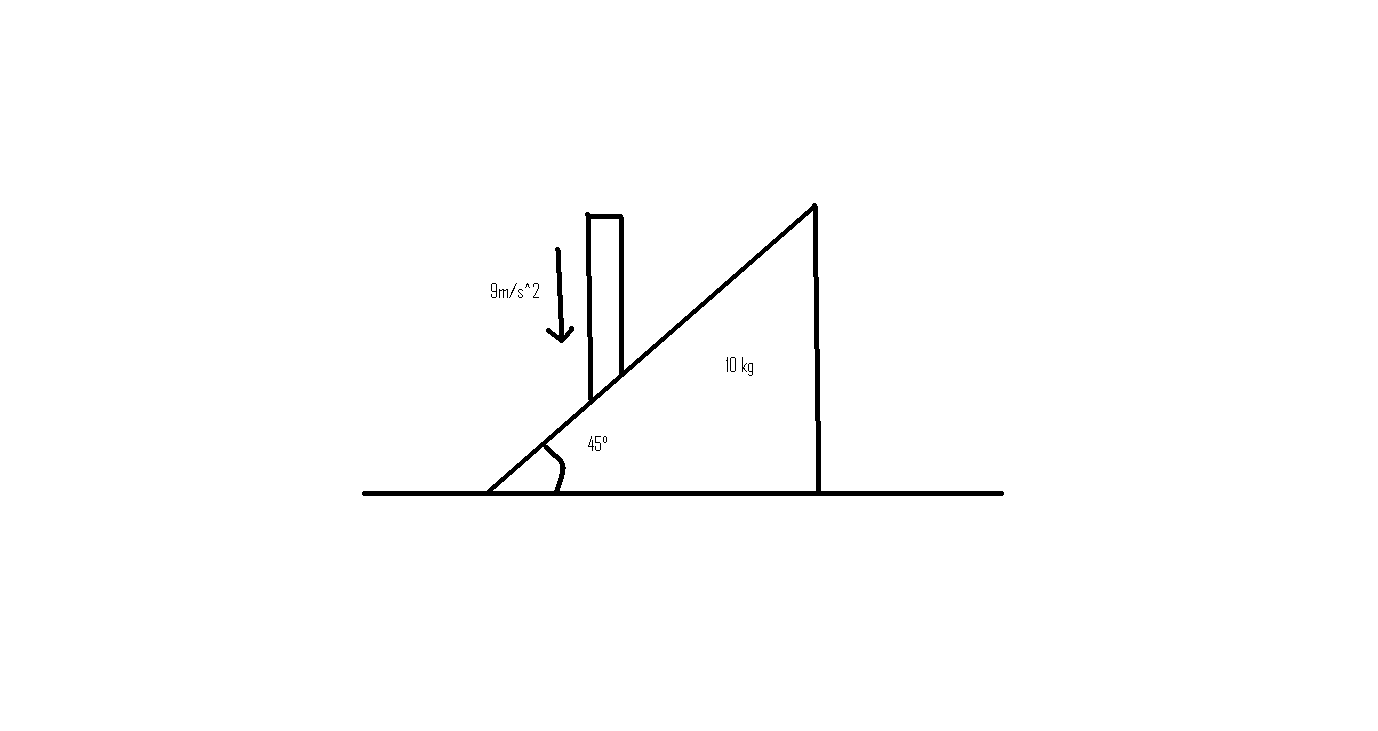
To determine the force exerted on the rod by the wedge in the given system, we need to analyze the forces acting on the rod and apply Newton's laws of motion. Given that the rod is being accelerated downward at 9 m/s², we can start by identifying the relevant forces and applying some basic physics principles.
Understanding the Forces at Play
In this scenario, we have a rod that is being pushed downwards by an external force, resulting in an acceleration of 9 m/s². The rod is in contact with a wedge, and we need to find the force that the wedge exerts on the rod. Since all surfaces are smooth, we can assume there is no friction involved.
Identifying the Mass of the Rod
To find the force exerted by the wedge, we first need to know the mass of the rod. However, since the options provided (120N, 200N, 160N, 180N) suggest that we might be able to derive the force without knowing the mass directly, we can use the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
Applying Newton's Second Law
According to Newton's second law, the net force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = m * a). In this case, the force exerted by the wedge on the rod will counteract the weight of the rod and provide the necessary force for the downward acceleration.
Calculating the Force Exerted by the Wedge
Let’s denote the mass of the rod as m. The weight of the rod (W) can be expressed as:
- W = m * g, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²).
The total downward force acting on the rod due to the external agent is:
- F_external = m * a = m * 9 m/s².
Now, the net force acting on the rod can be expressed as the difference between the external force and the weight of the rod:
- Net Force = F_external - W = m * 9 - m * 9.81.
Setting the net force equal to the mass times the acceleration (which is 9 m/s²), we can rearrange the equation to find the force exerted by the wedge:
- m * 9 = m * 9.81 - F_wedge.
From this, we can deduce that:
- F_wedge = m * (9.81 - 9) = m * 0.81.
Finding the Numerical Value
Now, we need to find a way to relate this to the options provided. If we assume a mass for the rod, we can calculate the force exerted by the wedge. Let’s take a mass of 200 kg as an example:
- F_wedge = 200 kg * 0.81 m/s² = 162 N.
This value is close to one of the options, specifically 160 N. Therefore, if we consider the mass of the rod to be around 200 kg, the force exerted by the wedge would be approximately 160 N.
Final Thoughts
Based on the calculations and the assumptions made, the force exerted on the rod by the wedge is most likely 160 N, which corresponds to option c). This analysis demonstrates how to apply Newton's laws and understand the dynamics of forces in a system involving acceleration and contact forces.