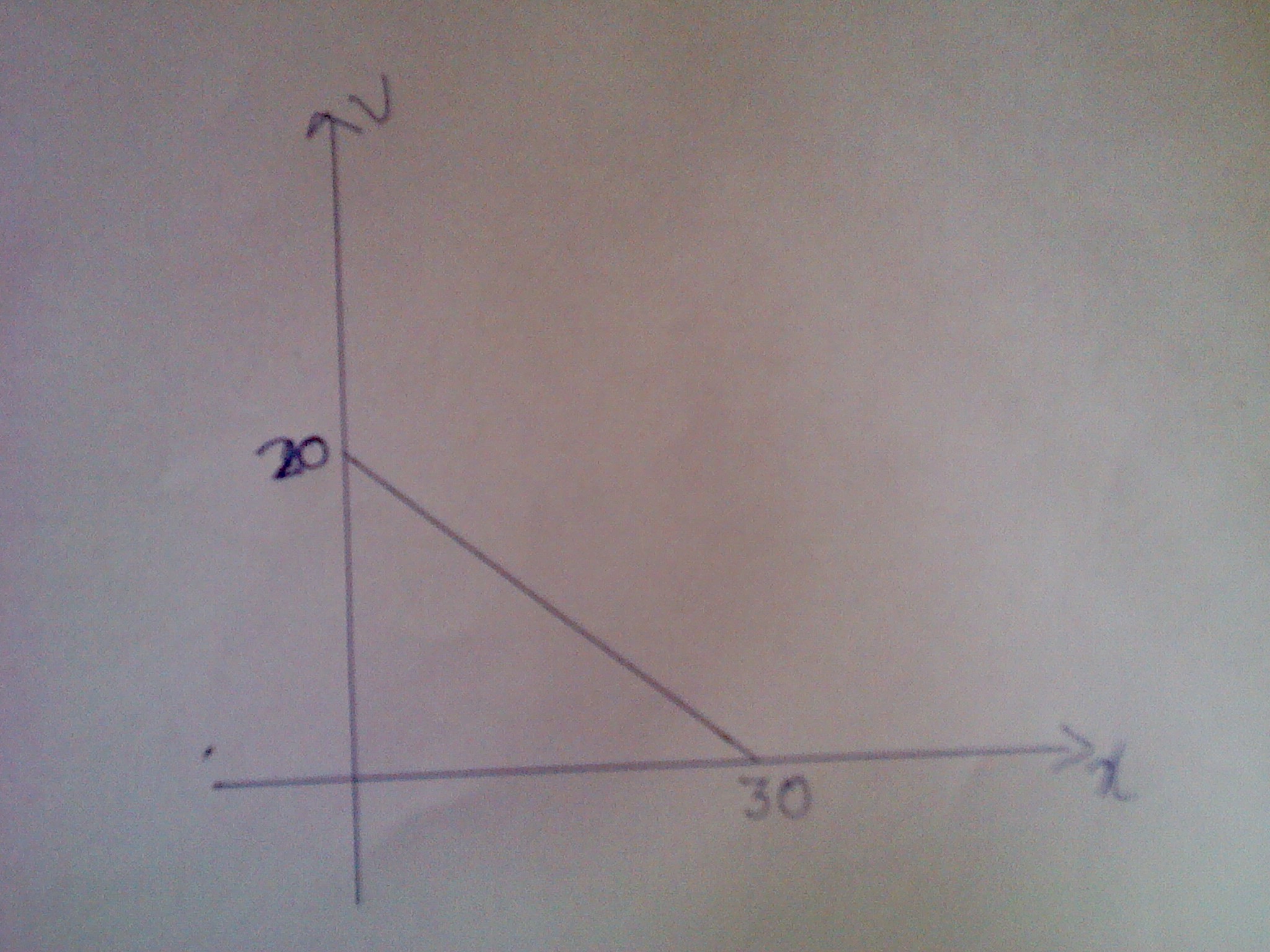
if the velocity v of a paticle moving along a straight line decreases linearly with its displacement from 20m/s to a value apporoaching zero at s=30m,determine the acceleration of the particle when s=15m.
if the velocity v of a paticle moving along a straight line decreases linearly with its displacement from 20m/s to a value apporoaching zero at s=30m,determine the acceleration of the particle when s=15m.