Invertebrates
Table of Content |
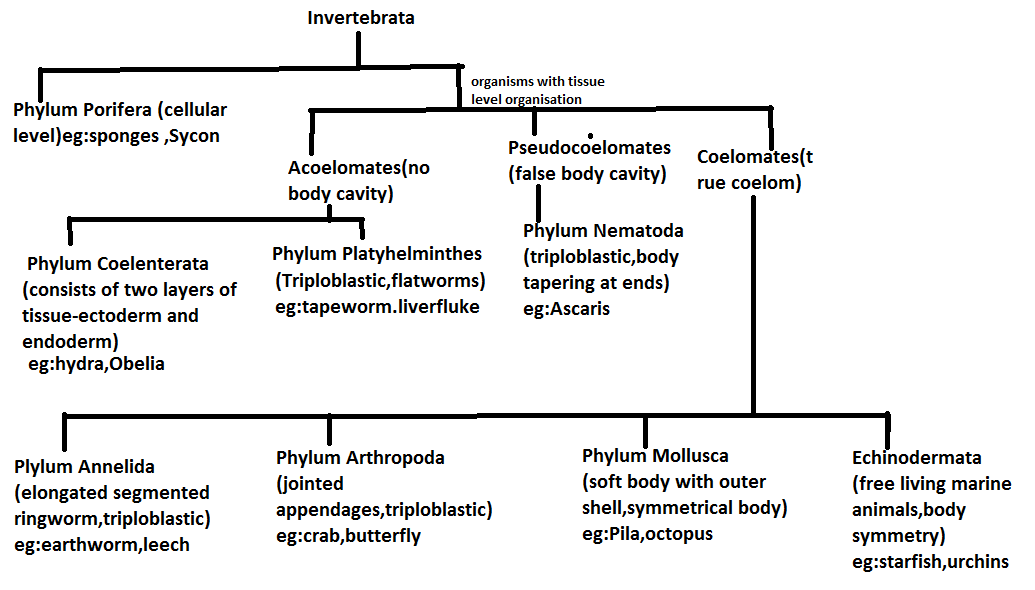
Definition of Invertebrates
Invertebrates (in·ver·te·brate) meaning: lacking a spinal cord or backbone, not vertebrate. Invertebrates are creatures which don't have a spine. Around 97% of all creatures are invertebrates. Nine phyla represent the list of invertebrates: Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Rotifera, Mollusca, Annelida, Arthropoda, & Echinodermata.
Classification of Invertebrates with Examples
1. Porifera- sponges
2. Cnidaria
a. sea anemones
b. hydra
c. corals
d. jelly‑fish
3. Platyhelminthes-flatworms
a. flukes
b. tapeworms
4. Nematoda-roundworms
a. Trichinella
b. Ascaris
c. hookworms
d. pinworms
5. Rotifera--rotifers
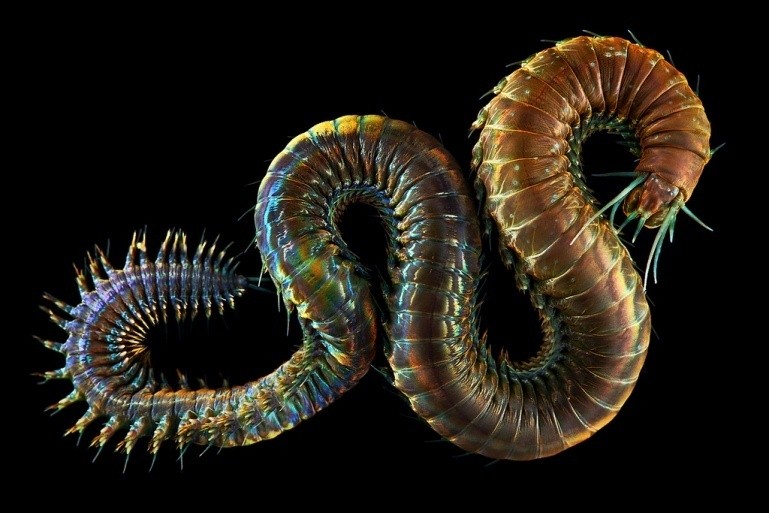
6. Annelida-segmented worms
a. earthworm
b. leeches
7. Mollusca-clams, oysters, snails, and octopus
-
Subphylum: Trilobita – Trilobites (extinct)
-
Subphylum: Chelicerata - Horseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites, & ticks
-
Subphylum: Mandibulata - Crustaceans, insects, millipedes, centipedes
9. Echinodermata: starfish, sea cucumbers, sea lilies
Sponges
Sponge
The phylum Porifera consists of sponges. There are around 800 distinct types of sponges, and 88% are marine. "Marine" implies that they live in salt water, for example, a sea or an ocean. Freshwater sponges are littler and less splendidly shaded than marine sponges. These are filter feeders. This implies they utilize their body as a channel to trap their sustenance, minute tiny fish.
Sponges are asymmetrically shaped and live appended to one spot as adults making them sessile creatures. Sponges comprise of a skeleton made out of an adaptable protein material called spongin and hard filaments called spicules made out of calcium carbonate or silicon dioxide. The body of a sponge is loaded with gaps or pore through which water enters their empty bodies. Sponges do not have the tissue level of association however they do have some particular cells. Choanocytes are particular cells that line pores in a sponge and have a flagellum that twists to pull in water and sustenance. Neckline cells at the base of choanocytes catch microscopic fish and begin processing it. Amebocytes are particular cells that convey sustenance to every single other part of a sponge's body. Squanders and abundance water leave a sponge through an opening at the top called the osculum.
Sponges duplicate asexually by internal or external buds and by the process of fragmentation at whatever point a bit of the sponge severs. Every piece can shape another sponge. This is the way sponges frame settlements. Sponges duplicate sexually by apportioning eggs and sperm into the water.
On the off chance that the freshwater supply dissipates, freshwater sponges get to be torpid and shape an internal bud or gemmule which is discharged when the sponge dies. The gemmule is a little freshwater sponge secured with solidified bodily fluid which keeps it from drying out. At the point when the freshwater gives back, the gemmule turns into a dynamic sponge.
Cnidarians
Cnidarian Diversity
The phylum Cnidaria incorporates ocean anemones, hydra, corals and jellyfish. All Cnidaria are marine with the exception of hydra, which is a freshwater living being. Cnidarians have spiral symmetry and are flesh- eating utilizing appendages that encompass their mouth to get nourishment. Cnidarians display two body shapes - the sessile polyp with arms and mouth at the top or the motile medusa with arms and mouth on the base. Cnidarians may exist in one of these two phases or experience both stages throughout their life cycle. Cnidarians have an empty gastrovascular pit within fixed with gastrodermis. Epidermis covers the outside and a jellylike material called mesoglea is between the layers. Mesoglea is thin in polyp shapes however thick in medusa frames. Cnidarians have stinging cells called nematocysts or cnidocytes on their appendages that are toxic and shoot out like a spear to slaughter or incapacitate prey. Their mouth is the main opening to their body so they have a two-way stomach related framework. The additionally have a straightforward nerve net. Cnidarians duplicate asexually by the process of budding or sexually creating fertilized eggs at whatever point males discharge sperm and females discharge eggs into the water. A few cnidarians like coral form a limestone case that makes a submerged reef.
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
The phylum Platyhelminthes are dorsoventrally smoothed and flattened and have a definite posterior end and anterioe end giving them a bilateral symmetry. Their bodies are strong so they are said to be acoelomate. A few flatworms are parasites, while others are free-living scroungers or carnivores. Examples of such flatworms include flukes and tapeworms. Flatworms additionally have just a mouth for both nourishment and discharging wastes. Their sensory system is made out of a nerve net and now and then eyespots that are light-sensitive at the foremost end. Particular flame cells dispose off wastes.
The Planarian is the most widely recognized free-living flatworm found in water or wet spots. They are bisexuals creating both eggs and sperm, yet they trade sperm with each other amid sexual proliferation. Planarians likewise reproduce asexually by fragmentation.
Flukes and Tapeworms frequently live in their host's stomach related tract impervious to the host's proteins. They lack a digestive system permitting the host to process their nourishment.
Tapeworms are partitioned into areas called proglottids that each have an entire reproductive framework creating fertilized eggs. Tapeworms are bisexual (one body having both sexual parts), and they prepare their own eggs. Ready proglottids with their eggs go out with the host=s dung. Tapeworms front end is known as the scolex and is adjusted with both snares and suckers to join to the host's digestion tracts. People frequently get tapeworms from undercooked pork, hamburger. on the other hand angle. Tapeworm eggs can withstand bubbling water so it is essential to cook these meats properly to obliterate the eggs. Children once in a while get tapeworms by playing with the excrement in the litter box of a feline, getting the eggs staring them in the face, and setting their hands or fingers in their mouth. The longest tapeworm ever gone by a man was 39 meters.
Flukes have complex life cycles that include more than one host. A fluke causes Schistosomiasis, an ailment that influences 250 million individuals around the world. This blood fluke assaults the kidneys, liver, and entrails bringing on dynamic shortcoming. It regularly takes 20 years to die due to Schistosomiases, and there is no cure till date.
Nematoda (Roundworms)
The phylum Nematoda comprises the roundworms. Roundworms are barrel shaped fit as a fiddle and vary from being minute to 20 inches long. Roundworms are pseudocoelomate having a body pit that is not totally lined.
Ascaris (round worm)
The pseudocoel that is the body cavity play the role of a hydrostatic skeleton with the help of which the muscles can contract. Dissimilar to flatworms, roundworms have a total gut. This implies they have a restricted digestive tract that is one way with a gut that starts with a mouth and finishes with an anus. Accordingly, they are generally ready to process nourishment. In any case, roundworms have no blood or heart. Supplements are circulated by a non blood liquid which is not pumped.
Most roundworms are parasites and are found in all natural surroundings. They are respectively symmetrical and unsegmented. Despite the fact that they are round and hollow, they for the most part taper at both body ends. They are secured with a thick defensive fingernail skin that is adaptable and can be shed. They have isolate genders for the most part and reproduce sexually.
The roundworm Trichinella, causes the disease called trichinosis. Individuals get trichinosis from eating undercooked pork. Trichinella gets into muscles and leaves calcium stores which impact muscle compression. Trichinosis can influence the heart. Another roundworm, Ascaris, parasitizes human lungs. The Filaria worm assaults the lymphatic framework creating incredible swelling. Hookworms and pinworms are likewise roundworms which parasitize people.
Rotifers
The phylum Rotifera incorporates minute worms found in aquatic and natural soil surroundings. At the head they have a crown of cilia encompassing their mouth for development and eating. Their bodies are secured with an external layer of chitin. Having separate genders, they reproduce sexually. A few animal categories contain just females and reproduce by parthenogenesis (unfertilized eggs forming into females).
Mollusks
The phylum Mollusca contains bivalves, octopus, snails and slugs, squid,and the chambered nautilus. Numerous individuals from this phylum have sturdy limestone shells and are found in all natural surroundings. Individuals from this gathering are monetarily essential as wellsprings of human nourishment, pearl and shell creation, flower and crop harm, pulverization to submerged wooden structures, and middle way host for some parasitic sicknesses. The mammoth squid and monster shellfish are the two biggest invertebrates. Mollusks comprise of bilateral symmetry and an instinctive mass containing their body organs. Mollusks additionally have a strong foot for development which can be altered into arms or limbs in a few animal types. Mollusks inhale through gills or lungs situated underneath a defensive layer called the mantle. The mantle frames the shell in a few animal categories furthermore ensures the body organs. All mollusks with the exception of bivalves contain a rasping, tongue-like radula for scratching sustenance. The circulatory framework comprises of a three-chambered heart and open-streaming framework with the exception of octopus and squids which have a closed circulatory framework. Multiplication is sexual even in bisexual structures. Mollusks experience a free swimming larval stage called the trochophore.
The class of mollusks called gastropods has a foot on their stomach. A case of a gastropod is the snail. At the point when a snail does not have a shell it is known as a slug. Snails and slugs stroll on their paunch. Most snails are marine, yet some do live on land. Marine snails have gills. Land snails are called pulmonate snails and have an air gap for relaxing. Snails can be huge. The protective cap snail can be as large as 15 pounds.
The class of mollusk called Bivalvia incorporates shellfishes, clams, mussels, and scallops. These mollusks have two shells pivoted together by a tendon. Solid adductor muscles open and close the shells. Incurrent and excurrent siphons circle water containing nourishment and oxygen through the bivalve. Gills separate the oxygen from the water, and they move by stream drive. Their solid foot can be reached out from the shell for development or tying down.
The class of mollusks called cephalopods has a foot on their head. Cases of cephalopods are octopus, squid and nautilus. Most cephalopods have mouths, arms and jaws and are dynamic predators. Their solid foot has been altered into arms or arms. They need external shells aside from the nautilus. These are the most savvy of all invertebrates. They utilized their siphons to move by fly impetus. Octopus has their shell within their body. Octopus secretes an inky substance which they release to help them escape from predators. The goliath squid is the biggest cephalopod. It may be up to 60 meters long and is well known to eat whales.
Annelids (Segmented Worms)
Annelid Polychaetes
The phylum Annelida comprises the segmented worms and is plentiful in all living spaces. External segments are portrayed by ring like structures along the body, and relating internal segments are called septa. Segmentation gives worms more adaptability in development and movement. If one segment is harmed, it is not generally lethal to the creature on the grounds that their organs are copied in different segments. Annelids have a tube inside a tube body arrangement known as a Coelom which is completely lined and contains the body organs. The coelom keeps running from the mouth to the anus. Annelids have bilateral symmetry, and a developed mind and various sense organs demonstrating cephalization. Coelomic liquid serves as a hydrostatic skeleton.
Worms have a place with this phylum. Every segment of the earthworm has setae or external abounds made of chitin. These abounds permit the earthworm to move and to tunnel into soil. Earthworms have a head and a central sensory system. Earthworms breathe through their moist skin as they burrow through the dirt and relax it. They have a closed circulatory framework in which blood is pumped by five sets of hearts. Most worms feast upon decaying vegetation making it break down quicker. A pharynx sucks in the natural trash which the strong gizzard grinds. Worms convey the supplements from the subsoil to the top soil, accordingly helping plants to develop. Undigested materials or castings are kept outside tunnels.
Bloodsuckers or leeches are likewise in the phylum Annelida. Most parasites live in water and have suckers at both finishes of their bodies. The tail suckers are utilized to hook on to a host, while the head suckers are utilized to suck blood from the host. Most bloodsuckers are predators or scroungers, however some suck blood. In view of this, parasitic bloodsuckers are gathered for anticoagulant. Leeches bodies are straightened dorsoventrally and need setae aside from one animal type. Like earthworms, bloodsuckers are bisexuals that trade sperm with different individuals from their species.
Polychaetes are marine annelids that comprise of setae changed into oar like structures called parapodia. Parapodia change development and give more territory for gas trades. Polychaetes regularly live commensally with sponges, mollusks, echinoderms, and shellfish. Genders are separate with external fertilization.
Arthropods
The individuals from the phylum Arthropoda all have jointed appendages. Truth be told, "arthropod" implies jointed leg. There are a greater number of types of arthropods than some other phylum. Arthropods have these attributes:
a. hard exoskeleton which is normally made out of substance called chitin
b. experience occasional ecdysis as they shed or shed their exoskeleton
c. they have specific body segments (head, thorax, cephalothorax, and midriff)
d. jointed extremities, for example, legs, receiving wire, and mouthparts.
e. open circulatory framework
The phylum Arthropoda is separated by sort of limbs. The subphylum Chelicerata has chelicerae or teeth and no antenna, while the subphylum Mandibulata has mandibles or jaws and antenna. Scavangers have pliers called chelipeds. The subphylum Trilobite is an extinct gathering with a head and trunk with a couple of legs on every segment.
Echinoderms
The phylum Echinodermata includes the starfish, sea urchins and sea cucumbers. The word "echinoderm" means spiny skin. These are the most advanced invertebrates.
Each and every other invertebrate are protostomes in which the blastopore amid their advancement transforms into the mouth. Echinoderms, like chordates, are deuterostomes in which the blastopore transforms into the rear-end. Echinoderms have an endoskeleton made out of convenient or settled calcium plates called ossicles. The people from this phylum have extended symmetry with a five segment body arrange. Grown-ups have no head or cerebrum and move by extendable tube feet. Echinoderms in like manner have a water vascular structure made up of a plan of canals that help the animal support and move. Water enters through an opening called the madreporite into a short stone channel into the ring trench. Outspread canals connect with the ring channel and choose the five-area symmetry. Such pressure driven water system is adequately strong to help starfish open mollusk shells. Skin gills are used for breathing and discharge. Echinoderms are prepared for expansive recuperation at whatever point parts are dropped. They can replicate agamically by discontinuity or sexually with outside fertilization.
Feather Starfish
Starfish are in the class Asteroidea and are dynamic marine predators with five arms set off from a focal circle and their mouth situated on the underside or oral surface. Bivalve mollusks are a most loved sustenance of the starfish, and they devour them by transforming their stomach back to front and staying it into the shellfish shell to process the mollusk.
Ocean urchins and sand dollars are in the class Echinodea and they need unmistakable arms. Five columns of tube feet distend through their skeletal. They utilize the spines of their skin and tube feet to move about and brush on green growth, coral, or dead fish. Triangular teeth around the mouth scrap or pound nourishment.
The class Crinoidea contains ocean lilies and plume stars with profoundly spread arms around their mouth for channel bolstering. Ocean lilies are joined by a stalk to the substrate, yet quill stars can segregate and move about.
Brittle stars of class Ophuroidea have thin arms appended to their focal plate and can move quicker than starfish. Ocean cucumbers are in the class Holothuroidea and are delicate, sluglike life forms with weathered external skin. Ocean cucumbers for the most part lie on their sides on the sea base and can discharge some portion of their entrails so as to frighten off a predator. They additionally move by tube feet or by squirming their whole body. Some of these are androgynous which is irregular for echinoderms.
Watch this Video for more reference